使用 Sentinel 应对突发流量,保护您的应用
在复杂的生产环境下可能部署着成千上万的 Dubbo 服务实例,流量持续不断地进入,服务之间进行相互调用。但是分布式系统中可能会因流量激增、系统负载过高、网络延迟等一系列问题,导致某些服务不可用,如果不进行相应的控制可能导致级联故障,影响服务的可用性,因此如何对流量进行合理的控制,成为保障服务稳定性的关键。
Sentinel 是阿里中间件团队开源的,面向分布式服务架构的轻量级流量控制产品,主要以流量为切入点,从流量控制、熔断降级、系统负载保护等多个维度来帮助用户保护服务的稳定性。
本文提供 Dubbo 整合 Sentinel 限流降级的最佳实践。
快速接入 Sentinel
Sentinel 通过对服务提供方和服务消费方的限流提升服务在极端场景下的可用性,接下来我们看看 Sentinel 对服务提供方和服务消费方限流的技术实现方式。
使用时我们只需引入以下模块(以 Maven 为例):
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-apache-dubbo3-adapter</artifactId>
<version>1.8.6</version>
</dependency>
<!-- optional -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-transport-simple-http</artifactId>
<version>1.8.6</version>
</dependency>
引入此依赖后,Dubbo 的服务接口和方法(包括调用端和服务端)就会成为 Sentinel 中的资源,在配置了规则后就可以自动享受到 Sentinel 的防护能力。
sentinel-apache-dubbo3-adapter中包含 Sentinel Filter 实现,加入依赖之后会自动开启。如若不希望开启 Sentinel Dubbo Adapter 中的某个 Filter,可通过配置关闭,如dubbo.provider.filter="-sentinel.dubbo.consumer.filter"。
示例详解
可在此查看以下 示例的完整源码。
Provider 端限流
对服务提供方的流量控制可分为 服务提供方的自我保护能力 和 服务提供方对服务消费方的请求分配能力 两个维度。
基于 QPS 设定限流
为了保护 Provider 不被激增的流量拖垮影响稳定性,可以给 Provider 配置 QPS 模式 的限流,这样当每秒的请求量超过设定的阈值时会自动拒绝多出来的请求。
以下是示例中配置的 服务级别 的 QPS 限流配置,最大 QPS 设定为 10:
// Limit DemoService to 10 QPS
FlowRule flowRule = new FlowRule();
// Note: the resource name here is the interface name.
flowRule.setResource(DemoService.class.getName());
flowRule.setCount(10);
flowRule.setLimitApp("default");
flowRule.setGrade(RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_QPS);
FlowRuleManager.loadRules(Collections.singletonList(flowRule));
以下是示例中配置的 方法级别 的 QPS 限流配置,最大 QPS 设定为 5:
// Limit sayHelloAgain method to 10 QPS
FlowRule flowRule = new FlowRule();
// Note: the resource name here includes the method signature.
flowRule.setResource(DemoService.class.getName() + ":sayHelloAgain(java.lang.String)");
flowRule.setCount(5);
flowRule.setLimitApp("default");
flowRule.setGrade(RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_QPS);
FlowRuleManager.loadRules(Collections.singletonList(flowRule));
启动消费端进程并持续发起调用,以下是限流生效后 provider 端打印的日志:
2018-07-24 17:13:43|1|com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.demo.dubbo.FooService:sayHello(java.lang.String),FlowException,default,|5,0
在 Provider 对应的 metrics 日志中也有记录:
1532423623000|2018-07-24 17:13:43|com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.demo.dubbo.FooService|15|0|15|0|3
1532423623000|2018-07-24 17:13:43|com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.demo.dubbo.FooService:sayHello(java.lang.String)|10|5|10|0|0
基于 QPS 限流(针对特定消费者)
上一节中的 QPS 限流值是针对所有消费端流量的,你也可以对来自特定消费端(以 dubbo 应用名识别)的 QPS 进行限流,通过设置 flowRule.setLimitApp("sentinel-consumer"); 即可,其中 sentinel-consumer 为发起调用的消费端应用名:
//......
// Note: this will take effect only for the specific consumer whose app name is "sentinel-consumer".
flowRule.setLimitApp("sentinel-consumer");
flowRule.setGrade(RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_QPS);
FlowRuleManager.loadRules(Collections.singletonList(flowRule));
在限流日志中会也会记录调用方的名称,如下面的日志中的 sentinel-consumer 即为调用方名称:
2018-07-25 16:26:48|1|com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.demo.dubbo.FooService:sayHello(java.lang.String),FlowException,default,demo-consumer|5,0
注意:为了使
limitApp生效,开发者需要调用调用RpcContext.getContext.setAttachment("dubboApplication", "sentinel-consumer")标识自己的身份,如果消费端引入了sentinel-apache-dubbo3-adapter则不需要额外调用以上方法了。
设置限流发生后执行的方法
调用 DubboAdapterGlobalConfig.setProviderFallback() 可以设置限流发生后的方法回调,这样就能在限流后做更多的定制动作。
DubboAdapterGlobalConfig.setProviderFallback((invoker, invocation, ex) -> {
System.out.println("Blocked by Sentinel: " + ex.getClass().getSimpleName() + ", " + invocation);
return AsyncRpcResult.newDefaultAsyncResult(ex.toRuntimeException(), invocation);
});
Consumer 端限流
对服务消费方的流量控制可分为 控制并发线程数 和 服务降级 两个维度。
并发线程数限流
推荐给 Consumer 配置线程数模式限流,来保证自身不被不稳定服务所影响。采用基于线程数的限流模式后,我们不需要再显式地去进行线程池隔离,Sentinel 会控制资源的线程数,超出的请求直接拒绝,直到堆积的线程处理完成,可以达到信号量隔离的效果。
以下方法设置消费端的最大并发线程数,方法 sayHelloConsumerFlowControl 的并发调用在超过 3 个线程时就会发生限流:
FlowRule flowRule = new FlowRule();
flowRule.setResource("org.apache.dubbo.samples.sentinel.DemoService:sayHelloConsumerFlowControl(java.lang.String)");
flowRule.setCount(3);
flowRule.setGrade(RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_THREAD);
FlowRuleManager.loadRules(Collections.singletonList(flowRule));
通过调用以下方法,可以设置限流发生时的回调方法(可选):
DubboAdapterGlobalConfig.setConsumerFallback((invoker, invocation, ex) -> {
System.out.println("Blocked by Sentinel: " + ex.getClass().getSimpleName() + ", " + invocation);
return AsyncRpcResult.newDefaultAsyncResult(ex.toRuntimeException(), invocation);
});
服务熔断降级
当服务依赖于多个下游服务,而某个下游服务调用非常慢时,会严重影响当前服务的调用。这里我们可以利用 Sentinel 熔断降级的功能,为调用端配置基于平均 RT 的降级规则。这样当调用链路中某个服务调用的平均 RT 升高,在一定的次数内超过配置的 RT 阈值,Sentinel 就会对此调用资源进行降级操作,接下来的调用都会立刻拒绝,直到过了一段设定的时间后才恢复,从而保护服务不被调用端短板所影响。同时可以配合 fallback 功能使用,在被降级的时候提供相应的处理逻辑。
以下方法设置 sayHelloConsumerDowngrade 的降级策略,当接口调用失败率达到 70% 时,方法调用自动降级:
@Component
static class SentinelDowngradeConfig implements CommandLineRunner {
@Override
public void run(String... args) {
List<DegradeRule> rules = new ArrayList<>();
DegradeRule rule = new DegradeRule();
rule.setResource("org.apache.dubbo.samples.sentinel.DemoService:sayHelloConsumerDowngrade(java.lang.String)");
rule.setGrade(CircuitBreakerStrategy.ERROR_RATIO.getType());
rule.setCount(0.7); // Threshold is 70% error ratio
rule.setMinRequestAmount(100);
rule.setStatIntervalMs(30000); // 30s
rule.setTimeWindow(10);
rules.add(rule);
DegradeRuleManager.loadRules(rules);
}
}
Sentinel控制台
Sentinel 的控制台可以作为流量控制、熔断降级规则统一配置和管理的入口,同时它为用户提供了多个维度的监控功能。在 Sentinel 控制台上:
- 动态下发配置规则并实时查看流量控制效果
- 查看机器列表以及健康情况
应用如何接入控制台
接入 Sentinel 控制台的步骤如下(缺一不可):
- 按照 Sentinel 控制台文档 启动控制台
- 应用引入
sentinel-transport-simple-http依赖,以便控制台可以拉取对应应用的相关信息 - 给应用添加相关的启动参数,启动应用。需要配置的参数有:
-Dcsp.sentinel.api.port:客户端的 port,用于上报相关信息(默认为 8719)-Dcsp.sentinel.dashboard.server:控制台的地址-Dproject.name:应用名称,会在控制台中显示
这样在启动应用后就能在控制台找到对应的应用了。
控制台功能简介
- 单台设备监控:当在机器列表中看到您的机器,就代表着已经成功接入控制台,可以查看单台设备的设备名称、IP地址、端口号、健康状态和心跳时间等信息。
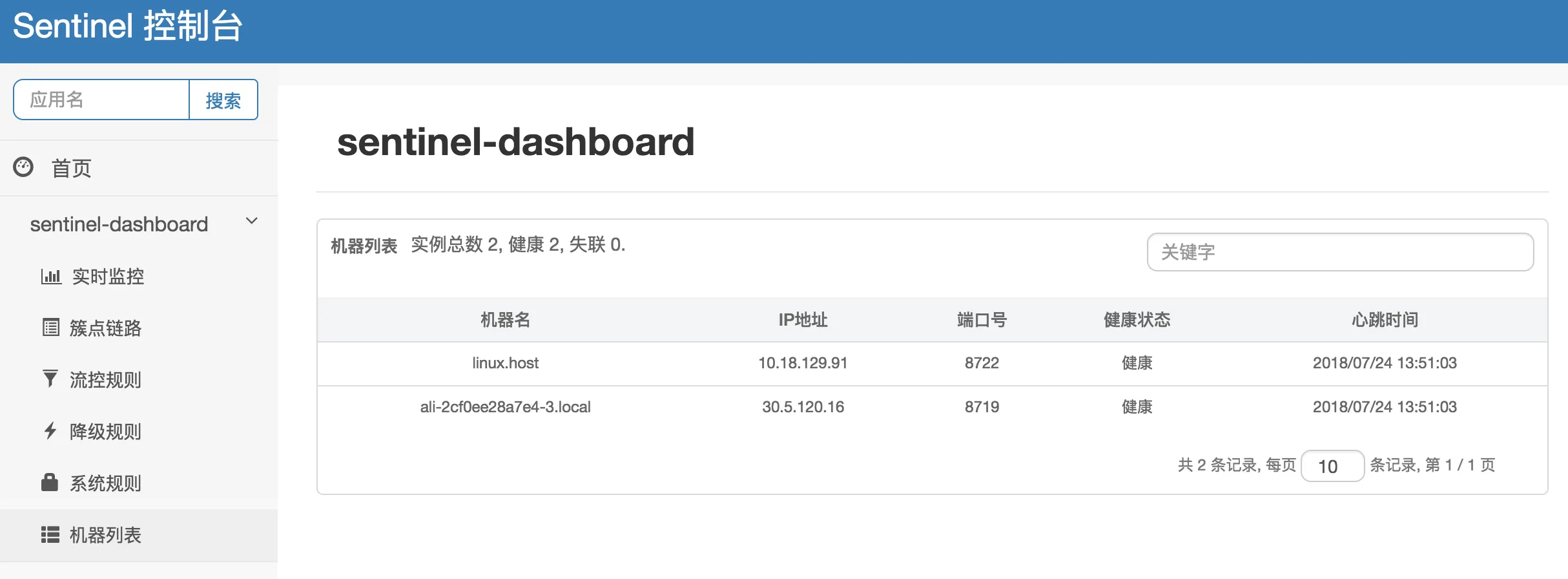
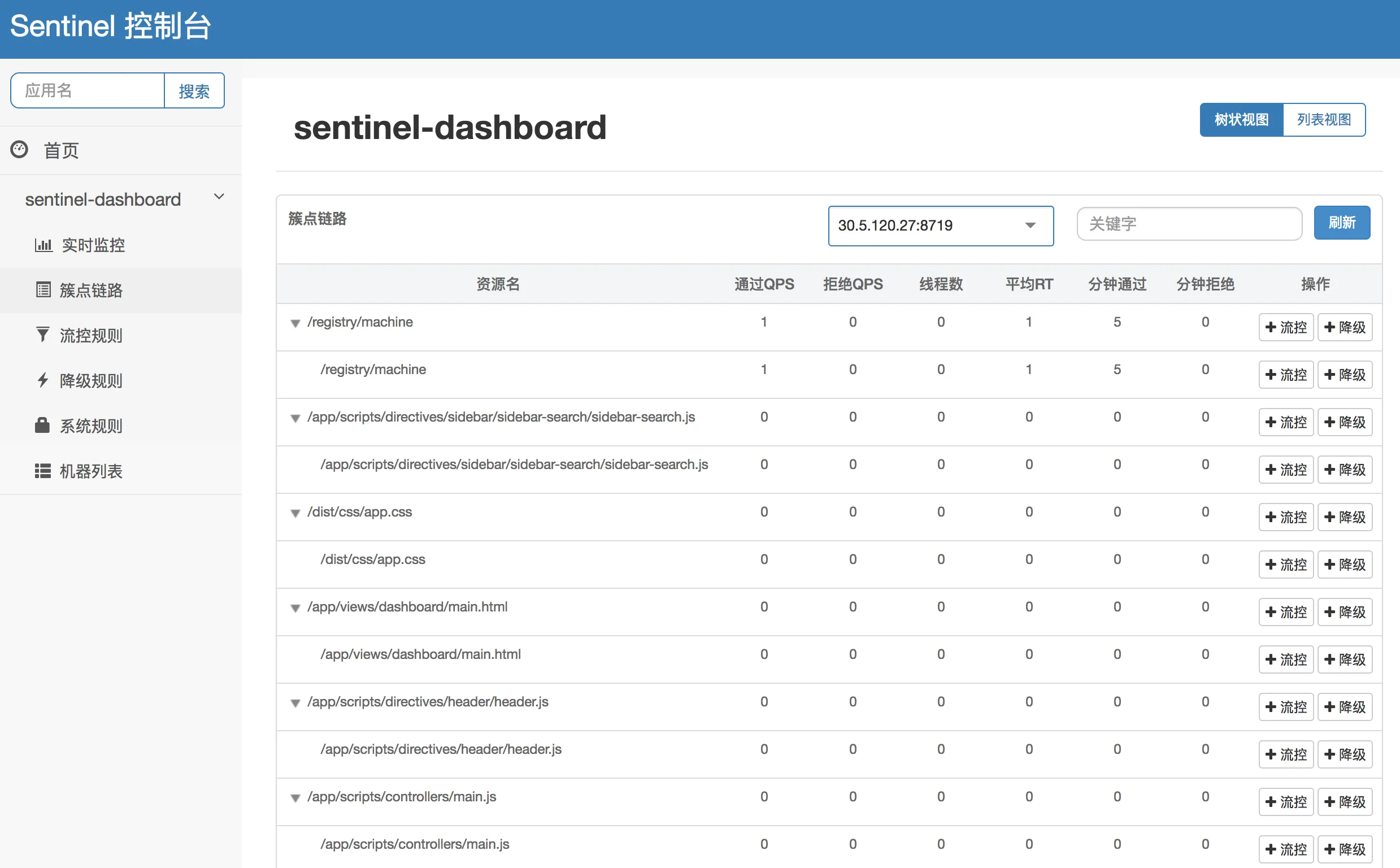
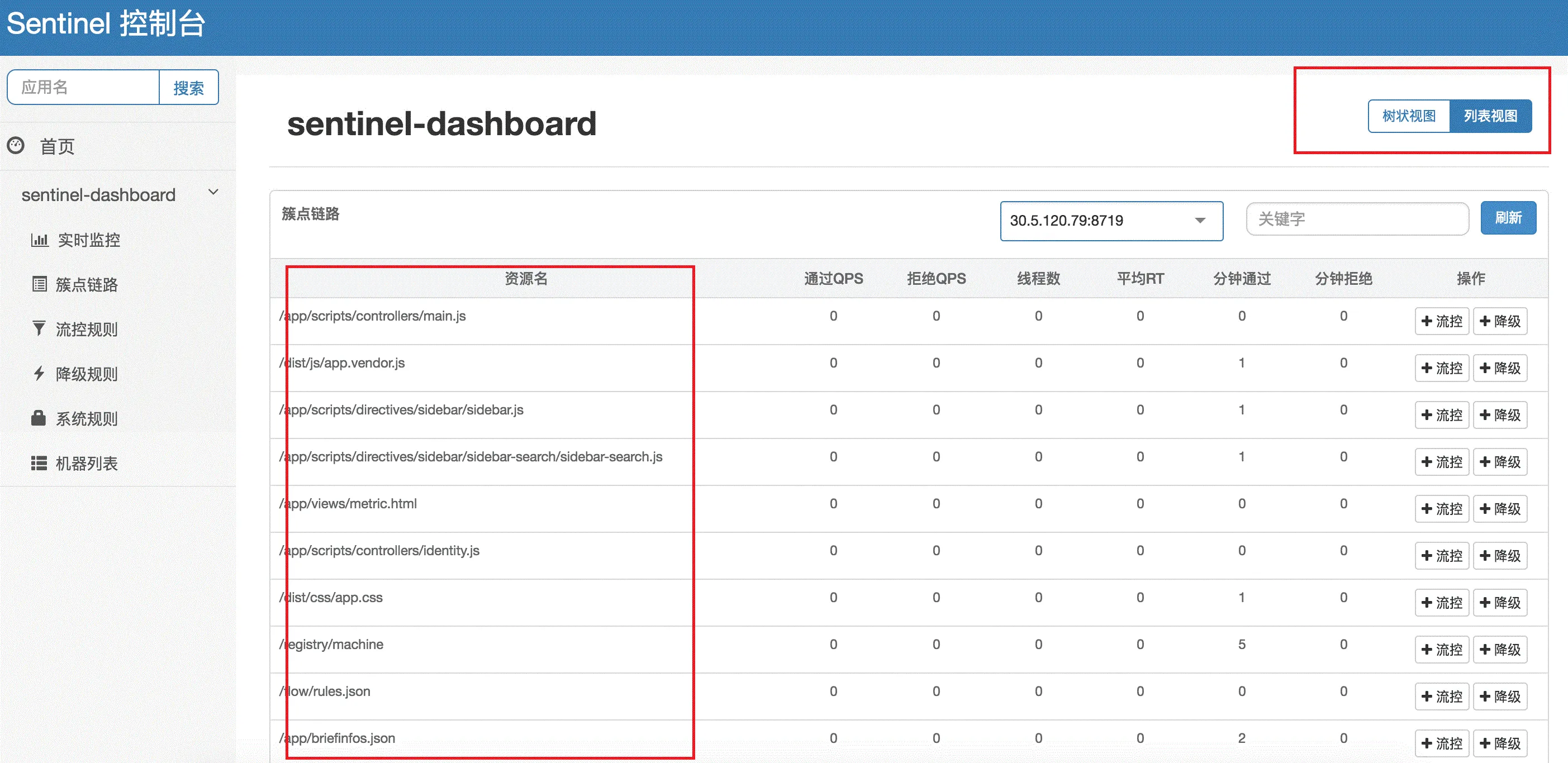
- 链路监控:簇点链路实时的去拉取指定客户端资源的运行情况,它提供了两种展示模式,一种用树状结构展示资源的调用链路;另外一种则不区分调用链路展示资源的运行情况。通过链路监控,可以查看到每个资源的流控和降级的历史状态。
树状链路
平铺链路
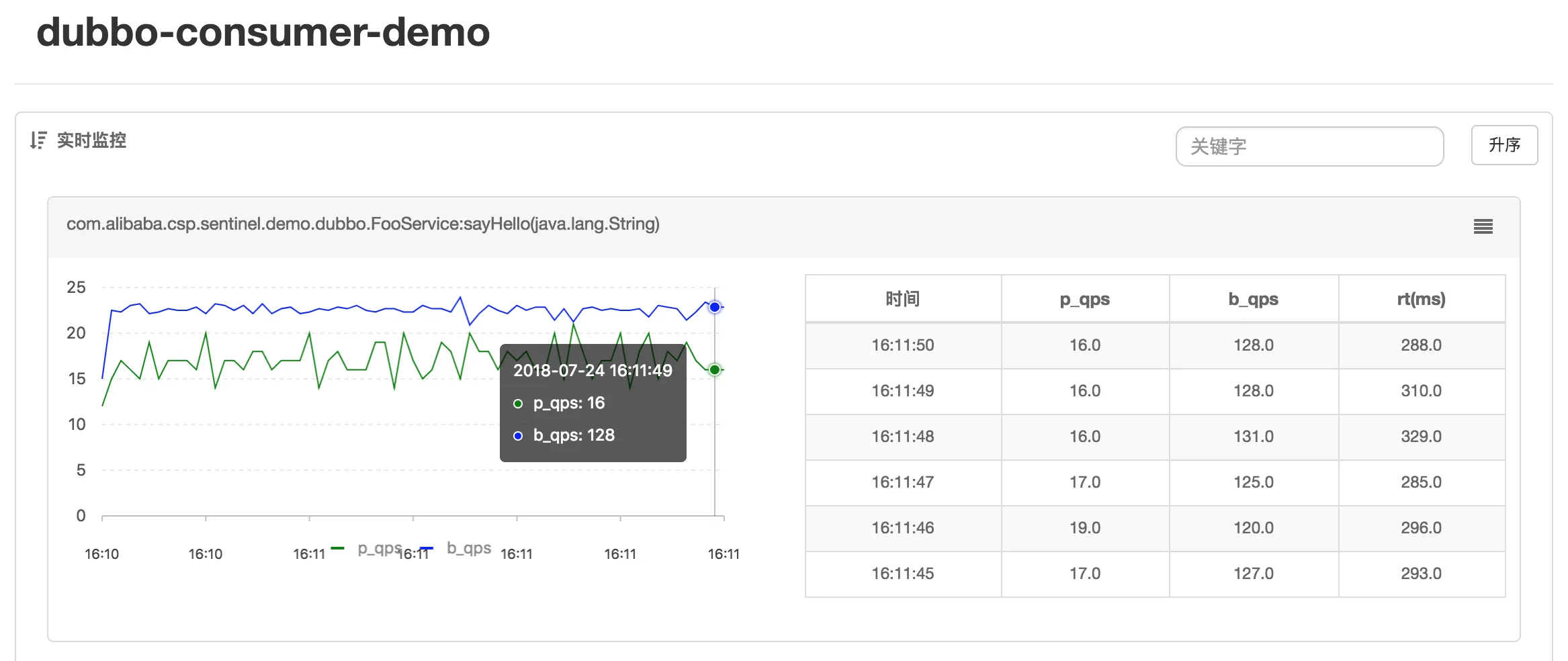
- 聚合监控:同一个服务下的所有机器的簇点信息会被汇总,实现实时监控,精确度达秒级。
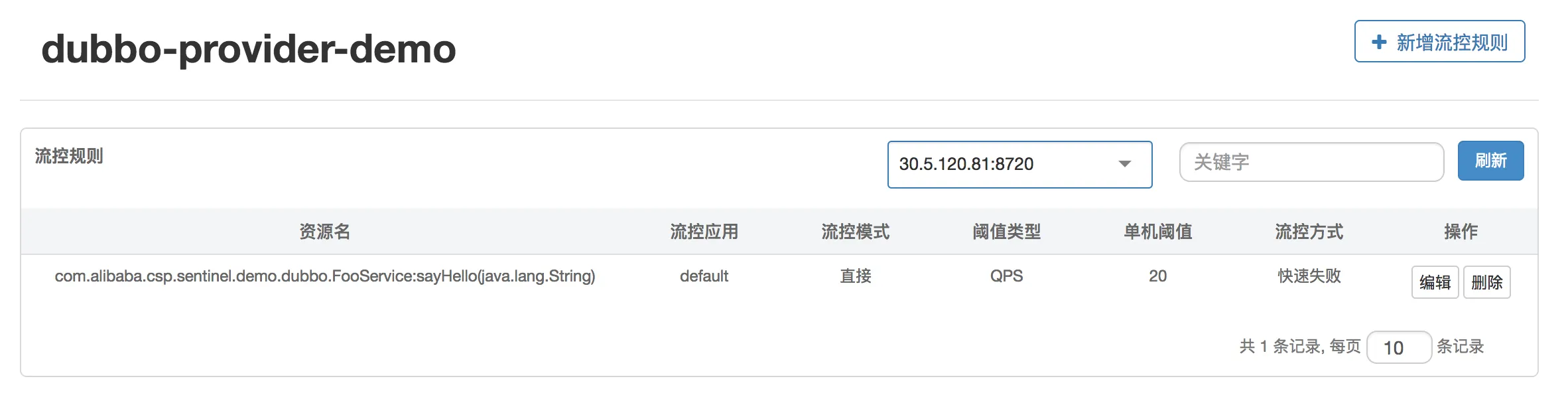
- 规则配置:可以查看已有的限流、降级和系统保护规则,并实时地进行配置。
参考链接
关于 Sentinel 的更多使用方式可以参考 Sentinel 官网