Dubbo2 Protocol Specification
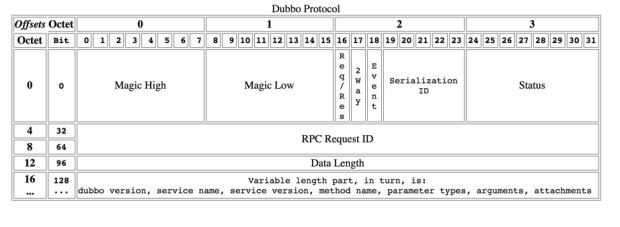
Protocol Specification
Magic - Magic High & Magic Low (16 bits)
Identifies the protocol version number, Dubbo Protocol: 0xdabb
Req/Res (1 bit)
Indicates whether it is a request or response. Request: 1; Response: 0.
2 Way (1 bit)
Only useful when Req/Res is 1 (request), marks whether a return value is expected from the server. Set to 1 if a return value from the server is needed.
Event (1 bit)
Indicates whether it is an event message, such as a heartbeat event. Set to 1 if this is an event.
Serialization ID (5 bit)
Identifies the serialization type: for example, the value for fastjson is 6.
Status (8 bits)
Only useful when Req/Res is 0 (response), used to identify the response status.
- 20 - OK
- 30 - CLIENT_TIMEOUT
- 31 - SERVER_TIMEOUT
- 40 - BAD_REQUEST
- 50 - BAD_RESPONSE
- 60 - SERVICE_NOT_FOUND
- 70 - SERVICE_ERROR
- 80 - SERVER_ERROR
- 90 - CLIENT_ERROR
- 100 - SERVER_THREADPOOL_EXHAUSTED_ERROR
Request ID (64 bits)
Identifies a unique request. Type is long.
Data Length (32 bits)
Length of the serialized content (variable part), counted in bytes. Type is int.
Variable Part
Each part serialized by a specific serialization type (identified by Serialization ID) is a byte[] or byte.
- If it is a request package (Req/Res = 1), each part is in order:
- Dubbo version
- Service name
- Service version
- Method name
- Method parameter types
- Method arguments
- Attachments
- If it is a response package (Req/Res = 0), each part is in order:
- Return value type (byte), identifying the type of value returned from the server:
- Return null: RESPONSE_NULL_VALUE 2
- Normal response value: RESPONSE_VALUE 1
- Exception: RESPONSE_WITH_EXCEPTION 0
- Return value: response bytes returned from the server.
- Return value type (byte), identifying the type of value returned from the server:
- If it is a request package (Req/Res = 1), each part is in order:
Note: For the (Variable Part), the current version of the Dubbo framework adds additional newline characters as separators between each content part when using JSON serialization, please add an extra newline after each part of the Variable Part, for example:
Dubbo version bytes (newline)
Service name bytes (newline)
...
Protocol Characteristics Analysis
Advantages
- The protocol is compactly designed; if it can be represented by 1 bit, it will not use a byte, for example, identifiers of boolean types.
- The headers for requests and responses are consistent, making it simple to implement with specific content assembled by the serializer.
Points for Improvement
Unfriendly for gateway proxy components. For HTTP requests, the resource to be accessed can be determined through headers, while Dubbo requires specific serialization protocols to resolve service names, methods, and method signatures. These locators are string types or string arrays, easily convertible to bytes and could be assembled into headers. Similar to HTTP/2 header compression, an int could be negotiated to identify RPC call resources, improving performance; if resource locators were assembled in the
header, this functionality would be easier to implement.Using req/res to determine if it is a request, the protocol can be fine-tuned, removing unnecessary identifiers and adding specific identifiers. For instance,
statusandtwoWayidentifiers can be strictly customized, removing redundant identifiers. Additionally, timeout is transmitted as a Dubboattachment, theoretically it should be placed in the request protocol’s header since timeout is essential in network requests. Notingattachment, it can be seen that some fields inattachmentduplicate existing fields in the protocolcontent, such aspathandversion, which increases protocol size.Dubbo converts the service name
com.alibaba.middleware.hsf.guide.api.param.ModifyOrderPriceParamtoLcom/alibaba/middleware/hsf/guide/api/param/ModifyOrderPriceParam;, which is unnecessary, adding only a;would suffice.The Dubbo protocol does not reserve extension fields, making it difficult to add new identifiers, thus affecting extensibility. For example, adding
response contextfunctionality can only be done by updating the protocol version number, which requires both the client and server versions to be upgraded, making it unfriendly for distributed scenarios.