Attention: The feature described in this doc is still under development or is in a very early stage, please keep updated!
Overall Architecture Design of Dubbo Admin Control Plane
1 Overall Architecture of Dubbo
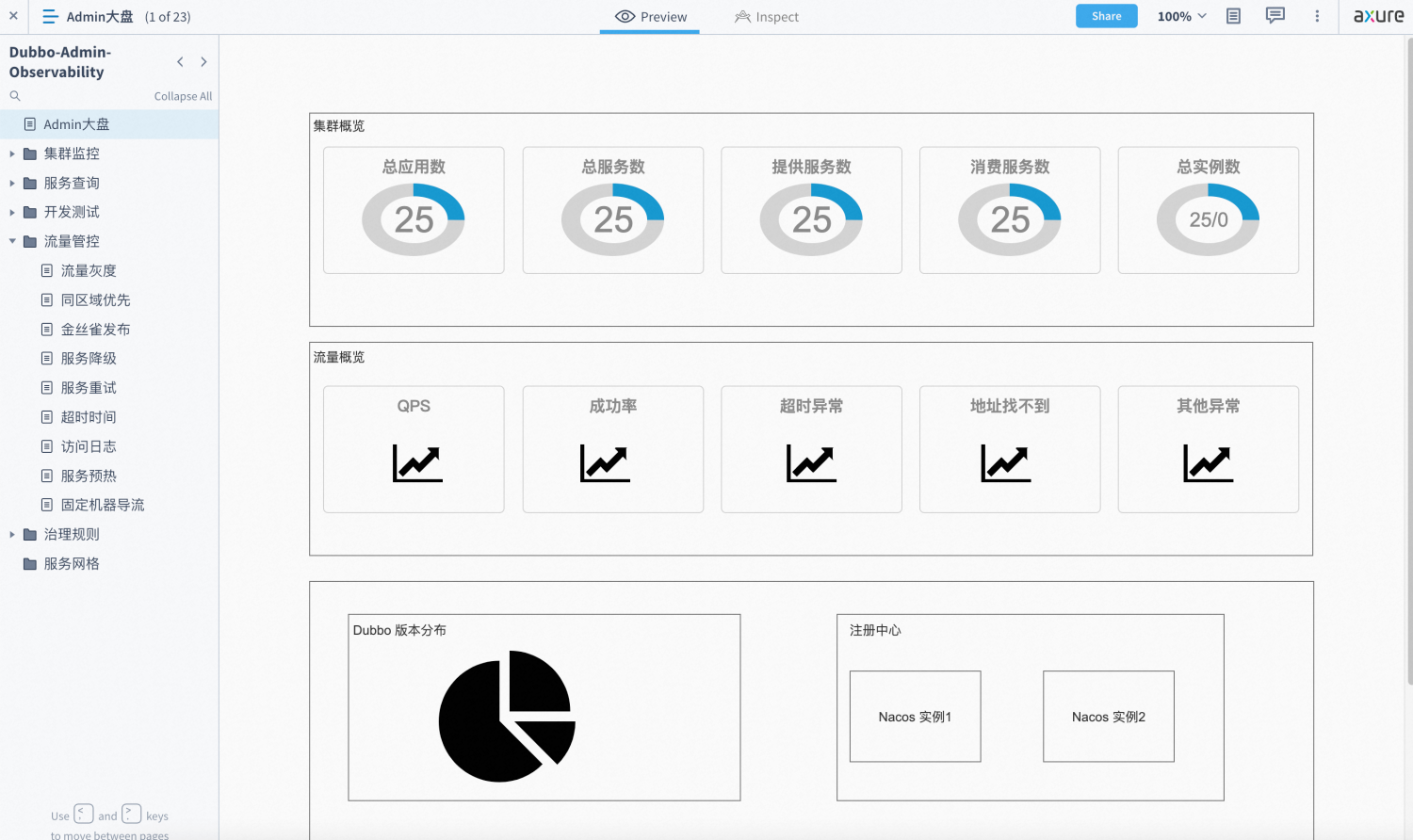
The architecture is divided into: Service Governance Abstract Control Plane and Dubbo Data Plane.
- Service Governance Control Plane. The control plane includes components such as the registry, traffic management strategies, Admin console, Istio, OpenSergo, etc.
- Dubbo Data Plane. The data plane represents all Dubbo processes in cluster deployment, which exchange data via RPC protocol and interact with governance strategies from the control plane.
Further explanation: https://cn.dubbo.apache.org/zh-cn/overview/what/overview/
Overall Positioning and Explanation of Dubbo Admin
Dubbo Admin is a unified definition and abstraction of the microservice governance system, providing uniform development and operation differences for microservice clusters deployed under different deployment architectures and infrastructure environments through custom core components and a series of supporting tools.
2 User-Oriented Development Steps
Step 1: Install Dubbo Stack/Admin
The core idea is to eliminate architectural differences by incorporating the installation and configuration of governance components into a prerequisite step in the Dubbo system through a unified entry point.
dubboctl install dubbo-stack
For installation, see: Dubbo Admin Installation Guide
Step 2: Service Framework Development
3 Control Plane Solutions

3.1 Identify Core Capabilities of the Dubbo Microservice Governance System
- Service Discovery
- Configuration Management
- Traffic Governance Rules
- Security Infrastructure
- Visualization Console
3.2 Unified Access Method for Service Governance Layer
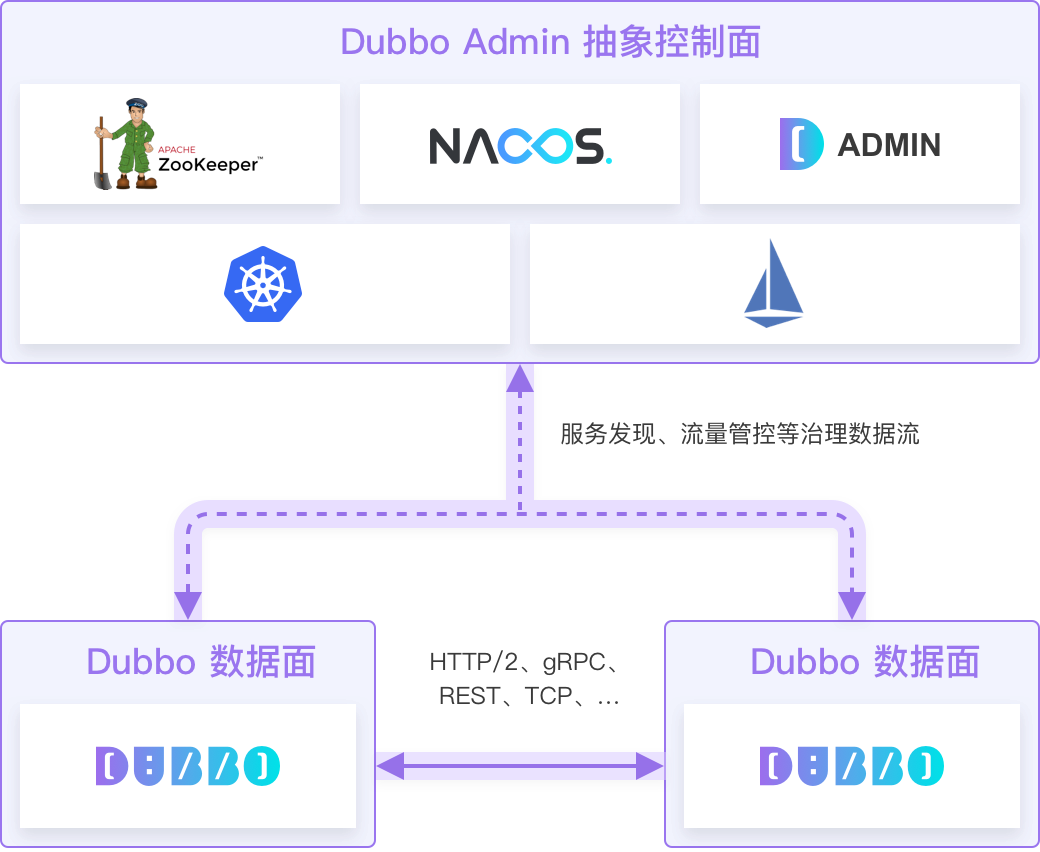
For any microservice deployment model, the Dubbo data plane uniformly targets **dubbo://hopst:ip** for programming the abstract service governance control plane.
Specific workflow:
- The data plane interacts with the admin component through configuration, and the admin returns the addresses of the actual registry, configuration center, and other components under the current deployment architecture, such as
nacos://host:port. - After receiving the new component addresses, the data plane component directly establishes communication with Nacos, relying on Nacos to complete service discovery and other functions.
3.3 How to Realize These Core Capabilities in Different Scenarios?
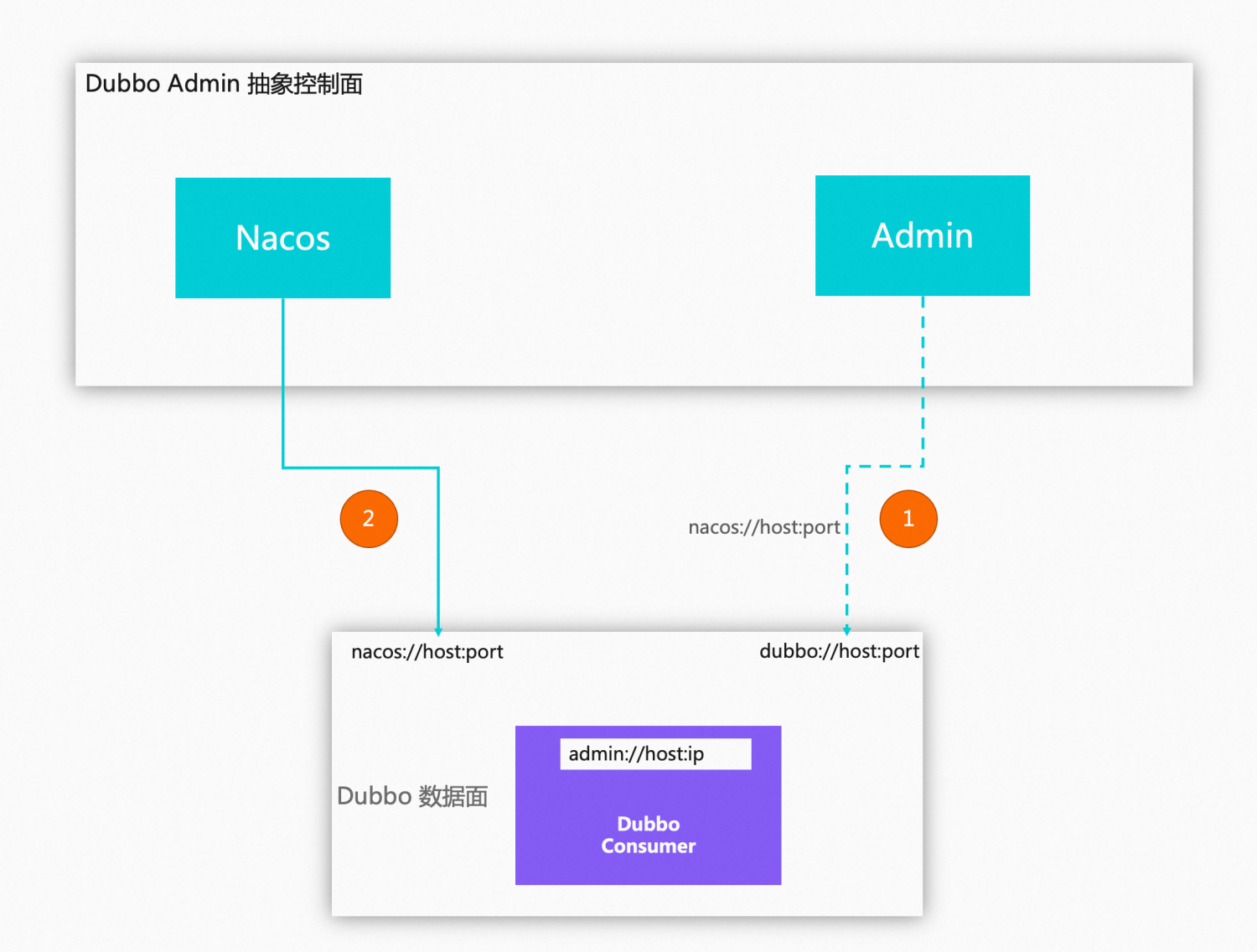
Scenario 1: Traditional Microservice System (VM & Kubernetes)
- One-click installation of control plane governance system (Admin & Nacos)
- Traditional Nacos service discovery and governance model
- The control plane can pull up more components as needed, such as Prometheus, etc.
Scenario 2: Kubernetes Service
- Istio Mode
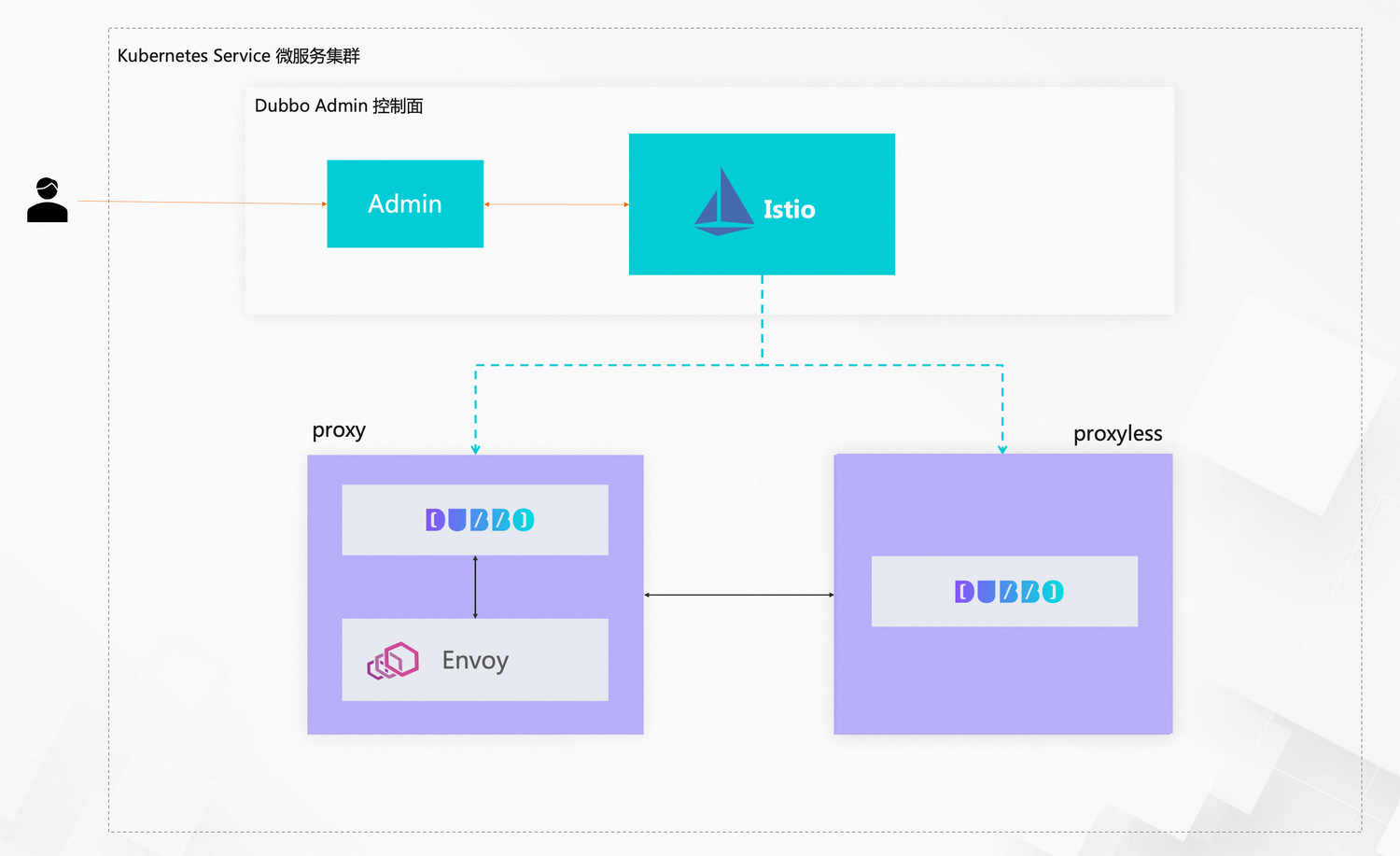
- Other Peer Modes Nacos/OpenSergo
Scenario 3: Migration or Multi-cluster
Clusters in isolated sub-network space
- 1
- 2
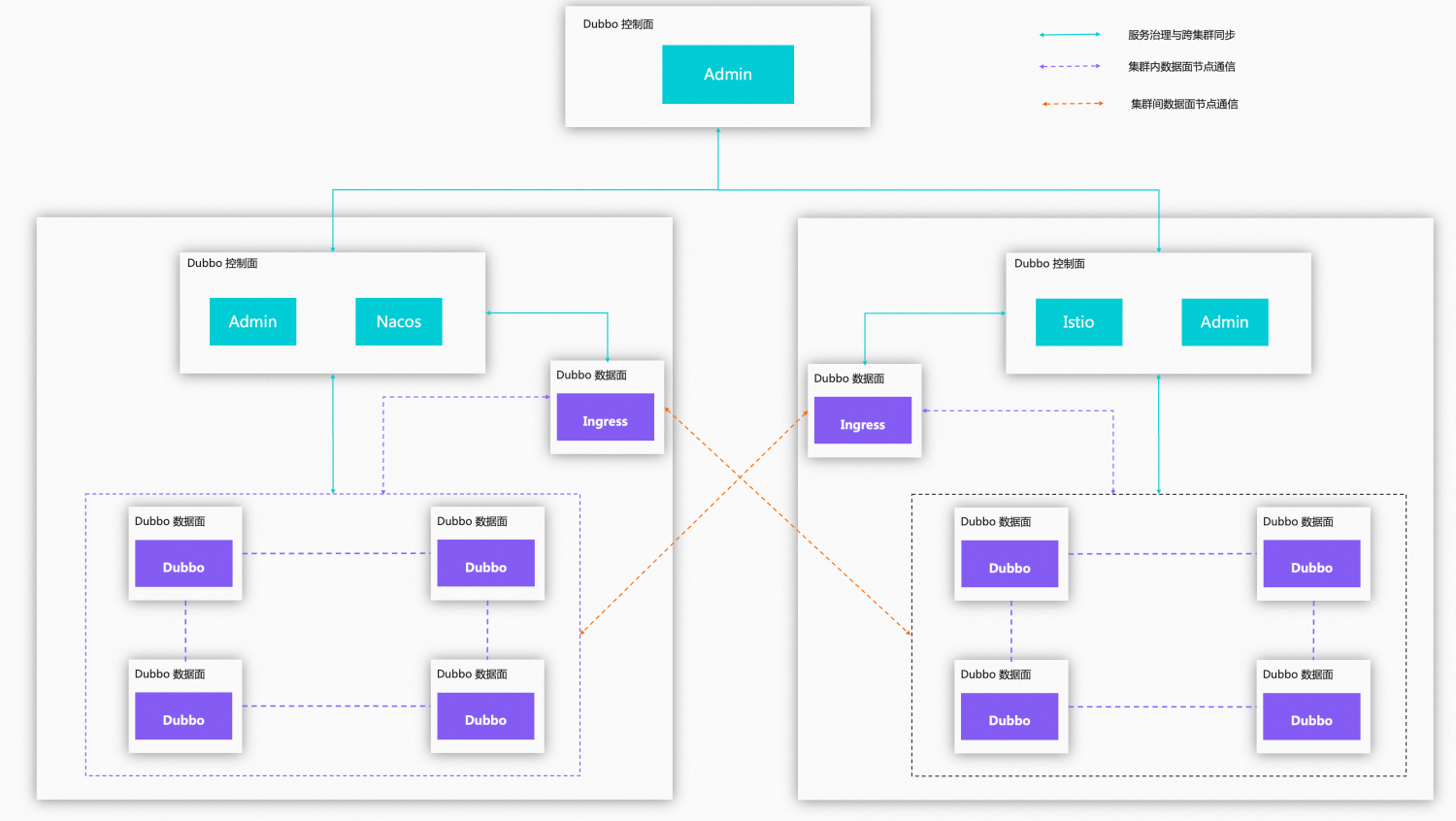
Clusters in the same network space
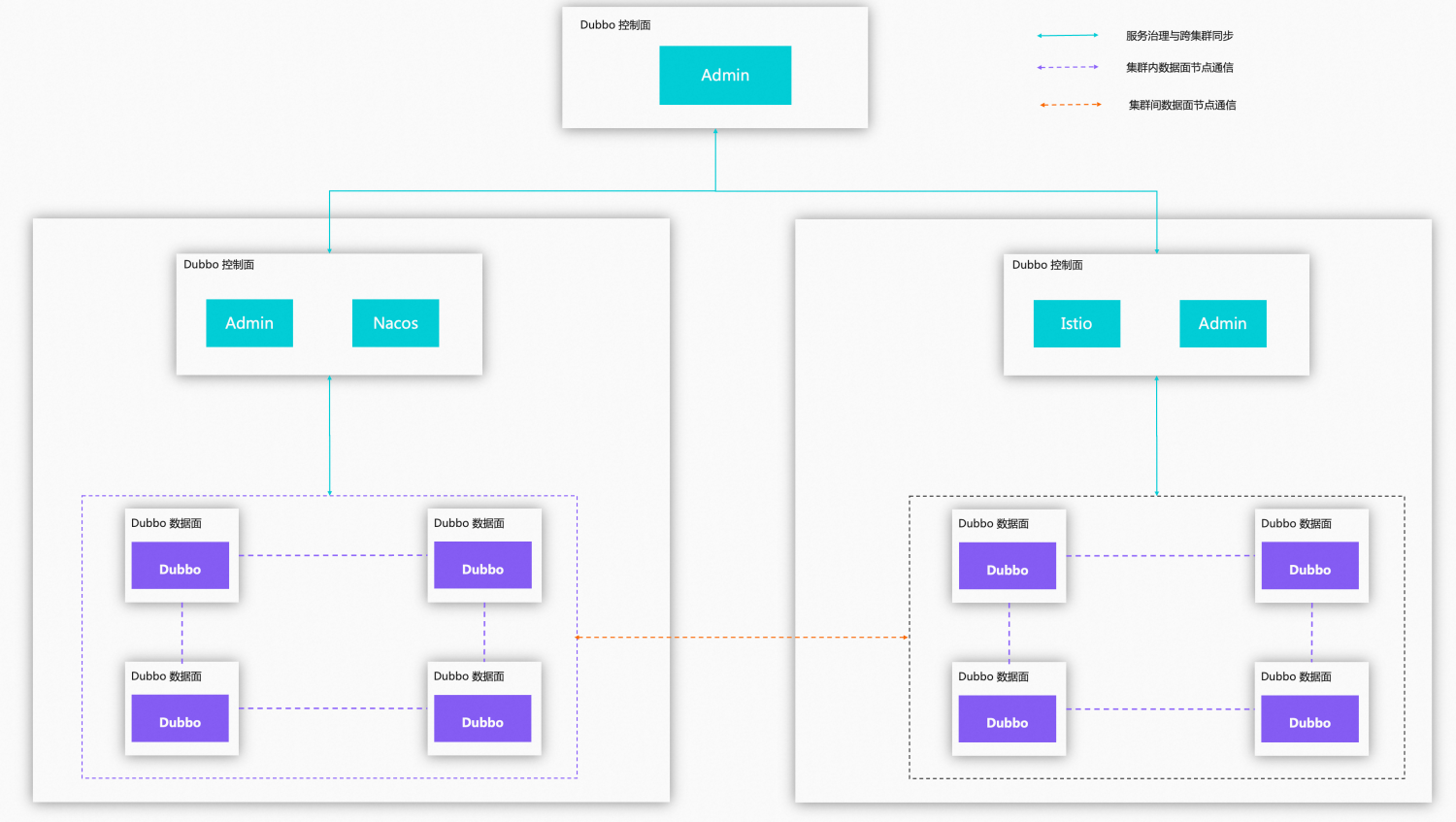
3.4 Admin Control Plane
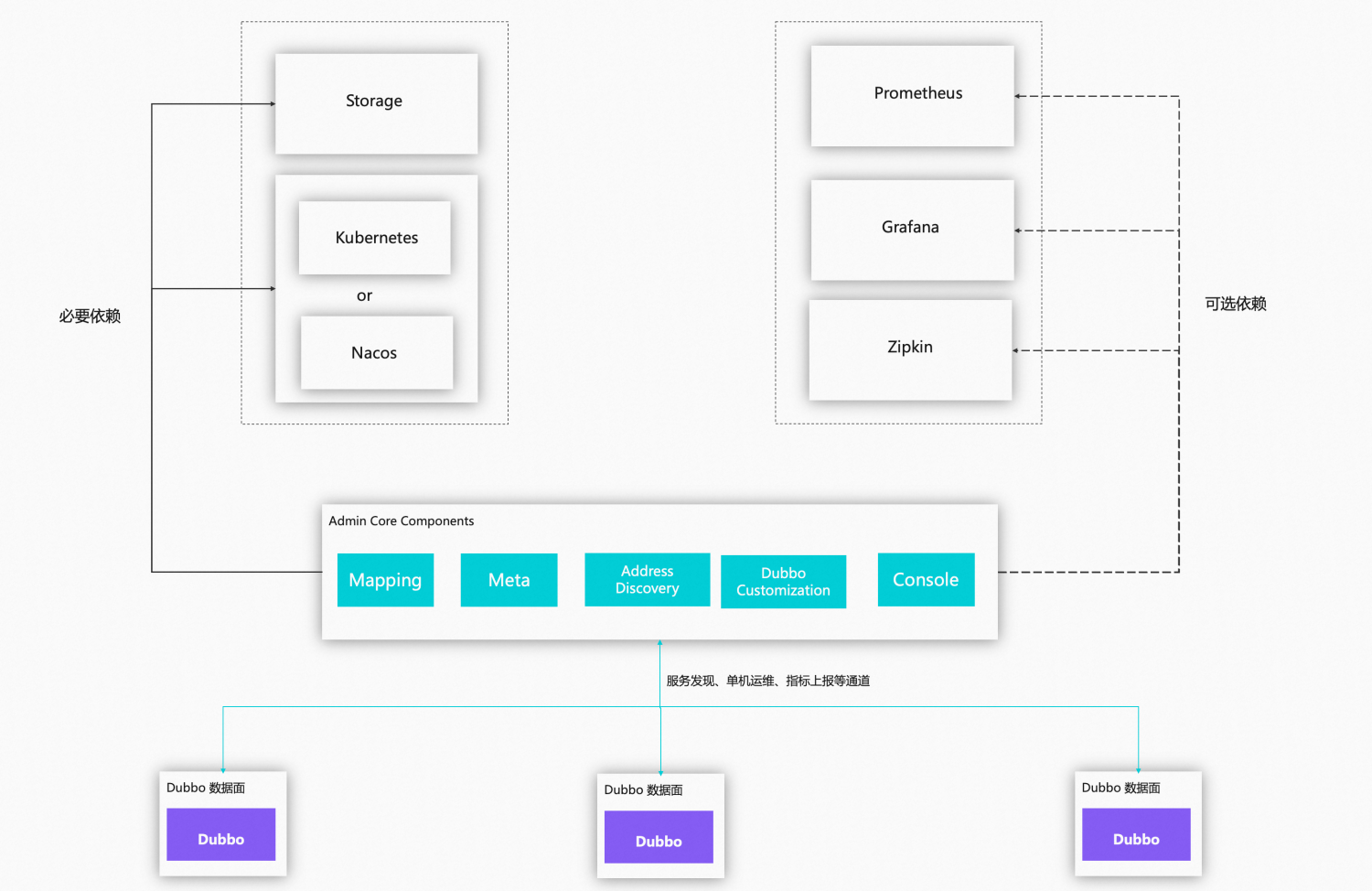
3.5 Other Supporting Infrastructures and Tools
User Console
Interactive address: https://qedzyx.axshare.com/#id=2pqh0k&p=admin__&g=1