Address not found exception
During the development and production deployment process, since Dubbo is a framework that requires service discovery for calls, it is easy to encounter No Provider exceptions due to various objective reasons. This article aims to provide a systematic troubleshooting approach to help you quickly locate and resolve the issue when exceptions occur.
java.lang.IllegalStateException: Failed to check the status of the service org.apache.dubbo.samples.api.GreetingsService. No provider available for the service org.apache.dubbo.samples.api.GreetingsService from the url consumer://*** to the consumer 30.221.146.226 use dubbo version 3.2.0-beta.4
Exception in thread "main" org.apache.dubbo.rpc.RpcException: No provider available from registry 127.0.0.1:2181 for service org.apache.dubbo.samples.api.GreetingsService on consumer 30.221.146.226 use dubbo version 3.2.0-beta.4, please check status of providers(disabled, not registered or in blacklist).
Summary in one sentence
When the service cannot be found, first check whether the service is fully developed and deployed, then corroborate whether it is registered in the registry, check the service side’s published status if registered, and consumer side’s subscription status if not registered. Any step along this way encountering issues will lead to exceptions.
Overview of troubleshooting thoughts
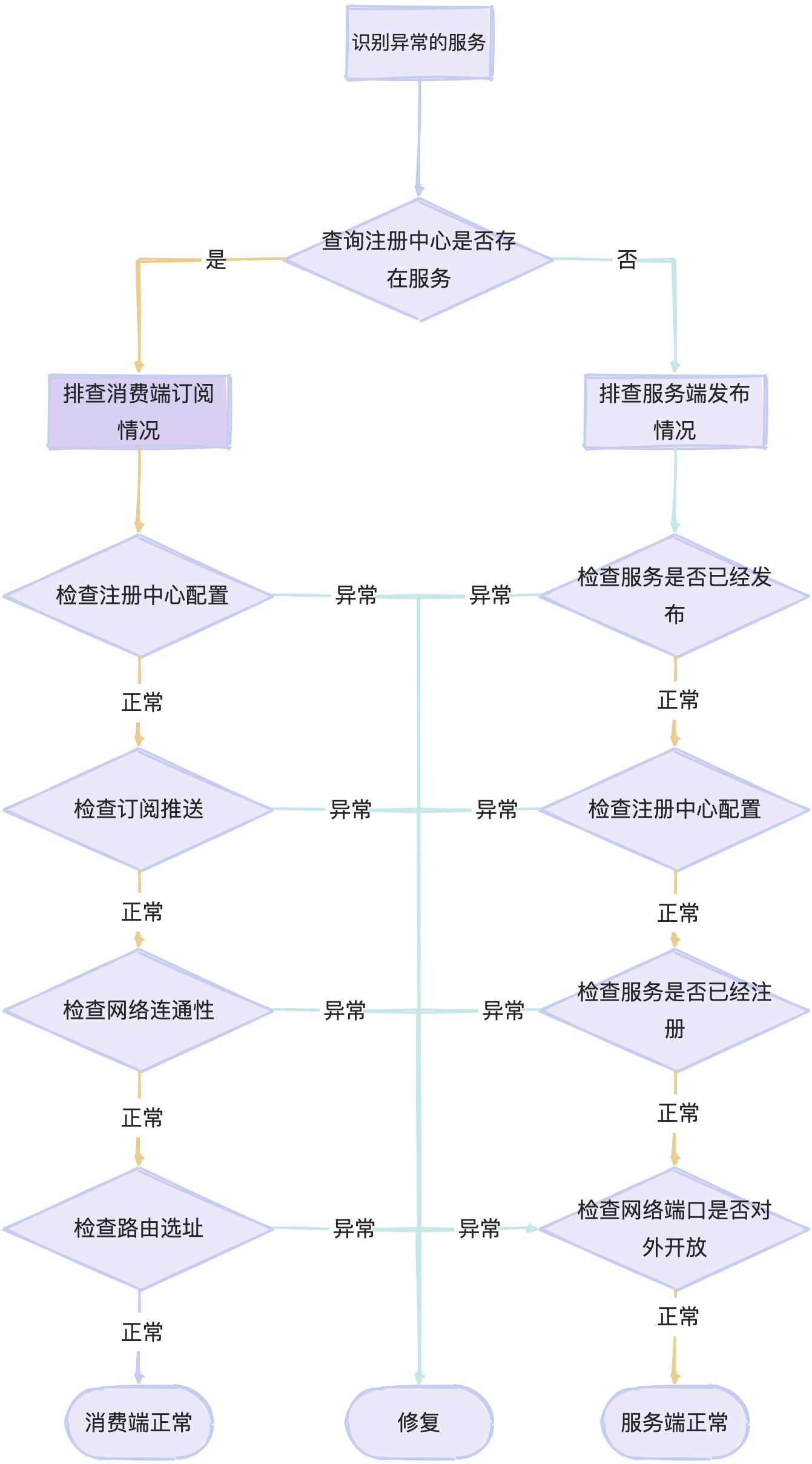
Detailed tutorial
1 Identify the problematic service and subscription mode
To correctly locate the direction of troubleshooting, the first step is to confirm the service name that reported the error.
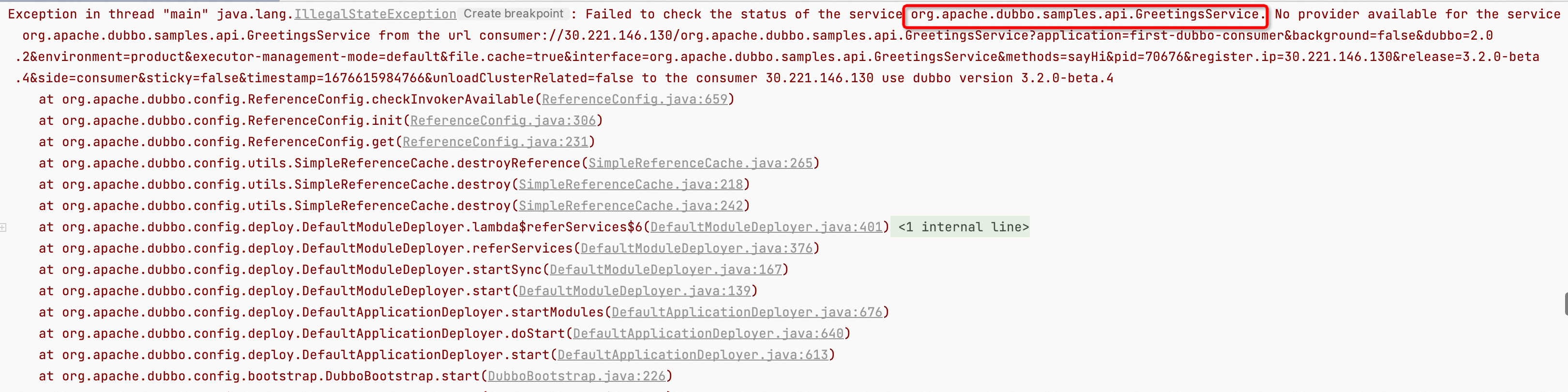
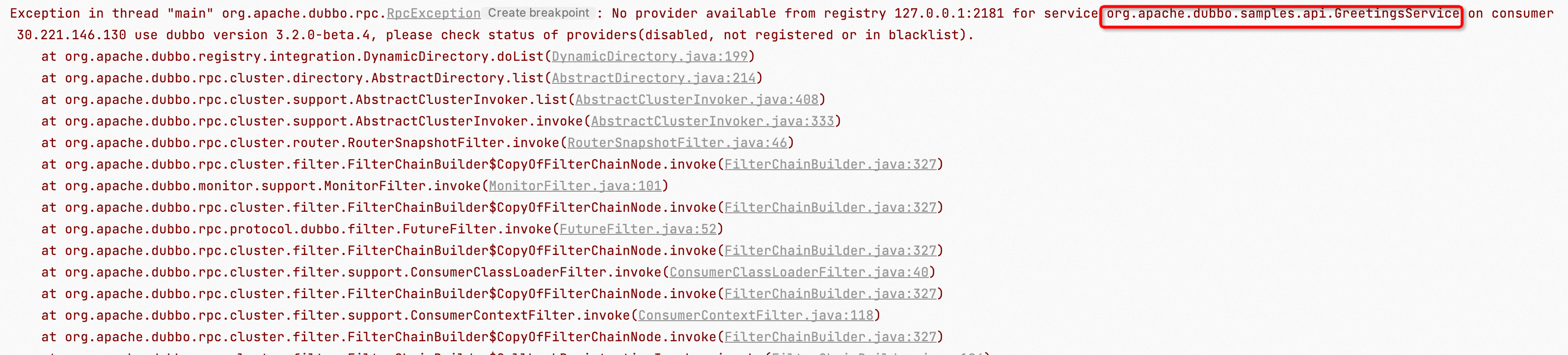
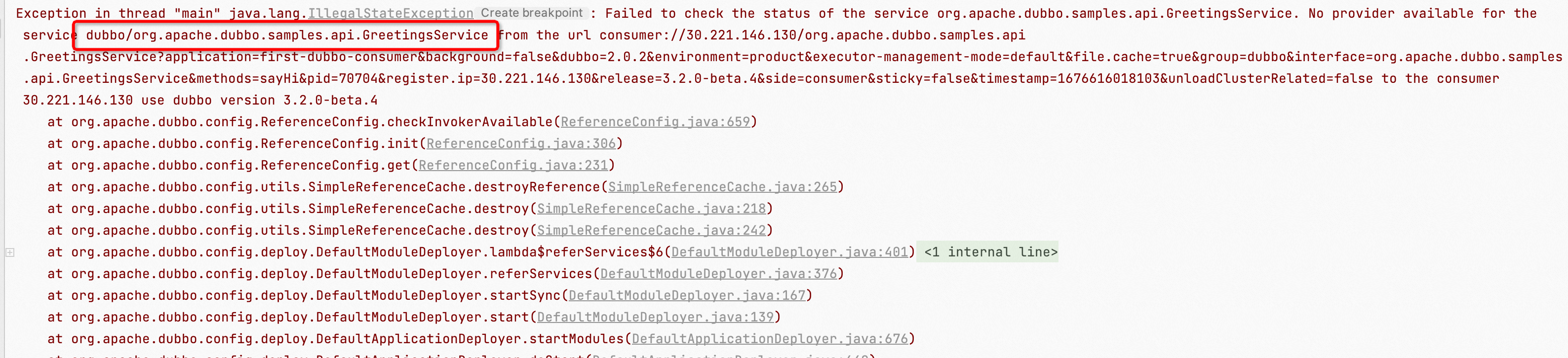
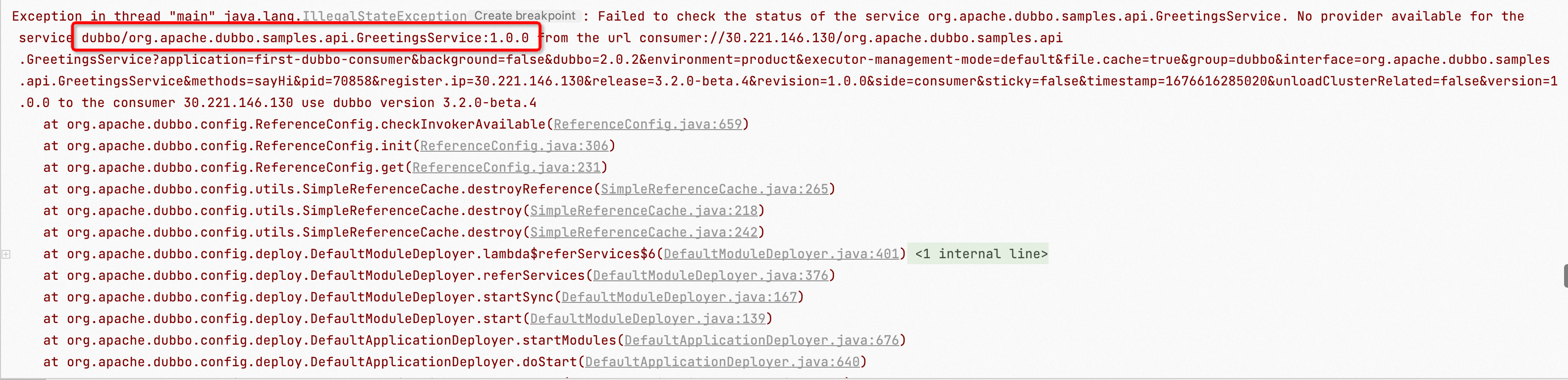
As shown in the images above, common address not found exception logs will include the corresponding service name, generally in one of the following two formats:
No provider available for the service ${serviceName}
No provider available from registry ${registryAddress} for service ${serviceName}
In this error log, the corresponding service name can be extracted. It is important to pay attention to the associated group and version number, usually formatted as follows:
${group}/${interfaceName}:${version}
In addition to extracting the service name corresponding to the error, the subscription mode of that service also needs to be obtained (usually defaults to APPLICATION_FIRST, that is, dual subscription mode).
For instance, in the following log, you can search for the keyword [DUBBO] Succeed Migrated to in Dubbo’s logs to obtain the corresponding subscription mode.
[26/02/23 03:27:07:007 CST] main INFO migration.MigrationRuleHandler: [DUBBO] Succeed Migrated to APPLICATION_FIRST mode. Service Name: org.apache.dubbo.samples.api.GreetingsService, dubbo version: 3.2.0-beta.6-SNAPSHOT, current host: 192.168.31.5
Currently, there are three subscription modes in Dubbo:
- FORCE_INTERFACE: Only subscribes to interface-level service discovery model data, which is the data model published in Dubbo versions 2.7.x and earlier.
- FORCE_APPLICATION: Only subscribes to application-level service discovery model data, which is the data model designed for cloud-native large-scale deployments starting from version 3.x of Dubbo.
- APPLICATION_FIRST: Subscribes to both interface-level and application-level service discovery model data; any model with available data can be invoked, prioritizing application-level service discovery data by default.
If the subscription mode of the problematic service is FORCE_INTERFACE, interface-level addresses must be checked during subsequent troubleshooting. If it is FORCE_APPLICATION, check application-level addresses instead. If it is APPLICATION_FIRST, any model’s published address will suffice.
2 Check if the service exists in the registry
2.1 Query through Dubbo Admin (recommended)
If Dubbo Admin is deployed in your cluster, you can directly check the registration status of the service in the “Service Query” module of the Dubbo Admin console.
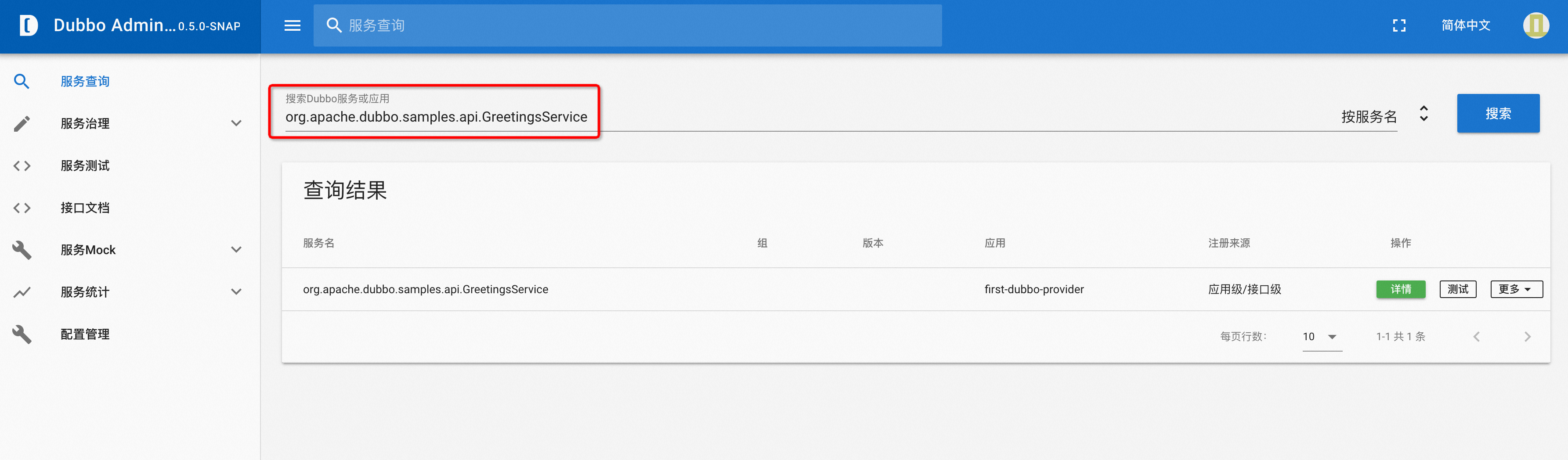
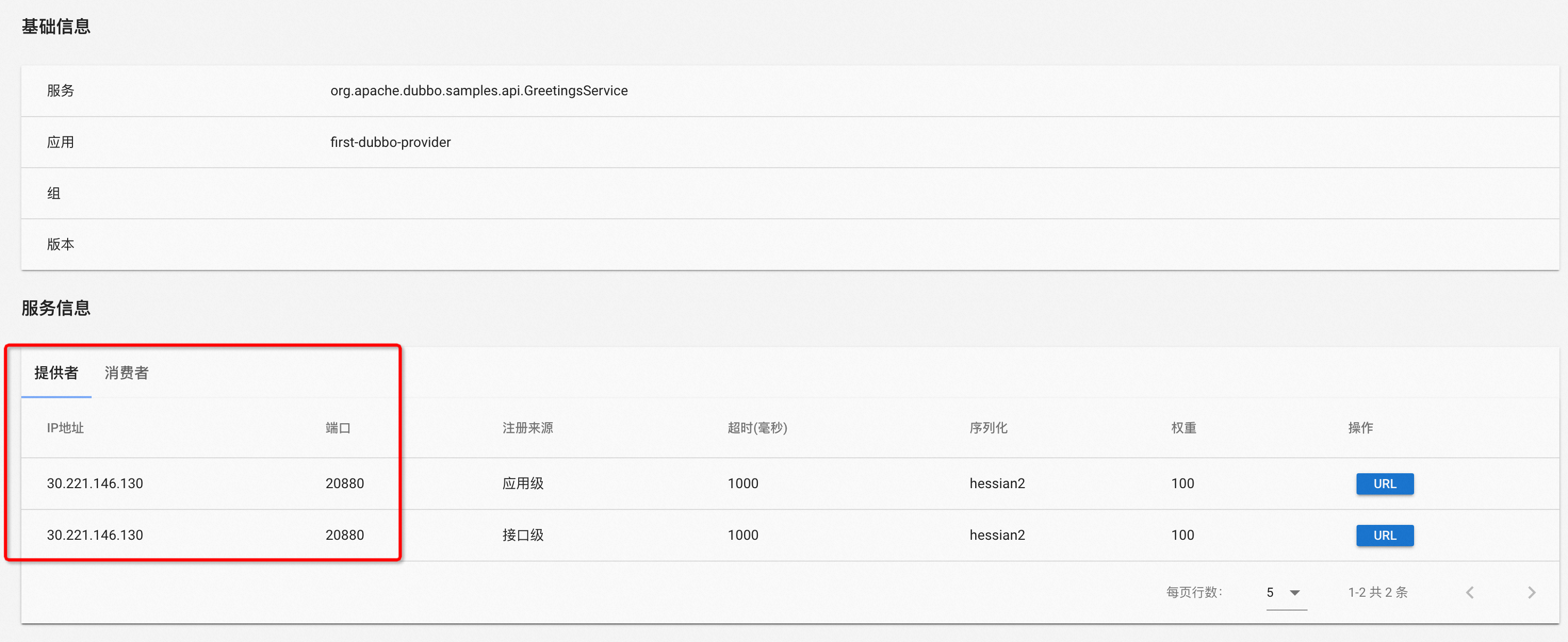
As shown above, please confirm whether you can find the expected service side in conjunction with the service discovery model established in Step 1. If found, proceed with Step x for further troubleshooting. If not found, move to Step 3 for troubleshooting.
2.2 Query through the registry
If you have not deployed Dubbo Admin, you can query the raw data directly through the registry.
2.2.1 Nacos Registry
1)Interface level service discovery In the interface-level service discovery model, you can directly query service information via the Nacos console by navigating to “Service Management” - “Service List” and searching by service name.
Note: In Nacos, the mapping relation of Dubbo service names to Nacos service names is providers:${interfaceName}:${version}:${group}, e.g., dev/com.example.DemoService:1.0.0 maps to providers:com.example.DemoService:1.0.0:dev.
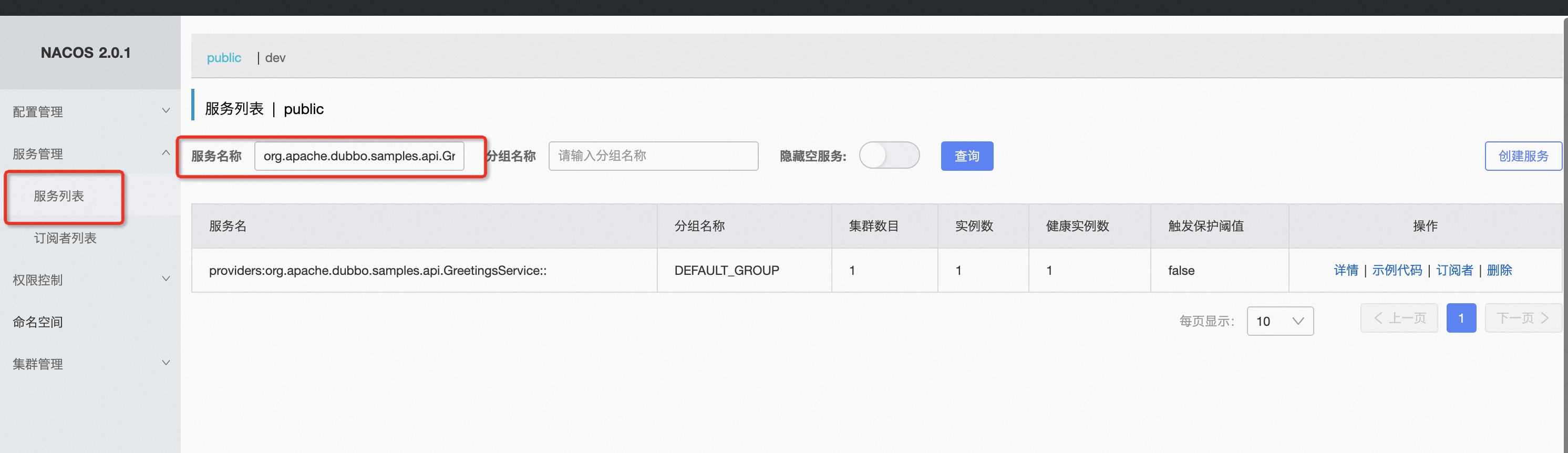
As shown above, please confirm whether you can query the expected service side in conjunction with the service discovery model established in Step 1. If found, proceed with Step x for further troubleshooting. If not found, move to Step 3 for troubleshooting.
2)Application level service discovery
In the application-level service discovery model, first check the mapping information of the service by navigating to “Configuration Management” - “Configuration List”, where Data ID is the interface name and the Group should be mapping.
Note: When checking service mappings, the Data ID is the interface name, and group and version numbers do not need to be filled.
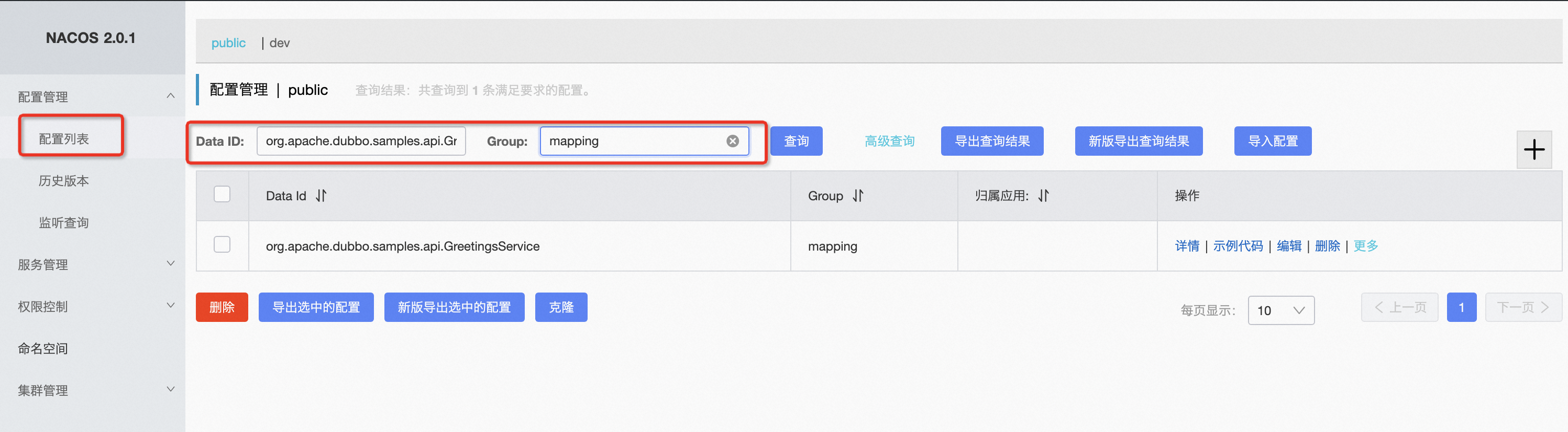
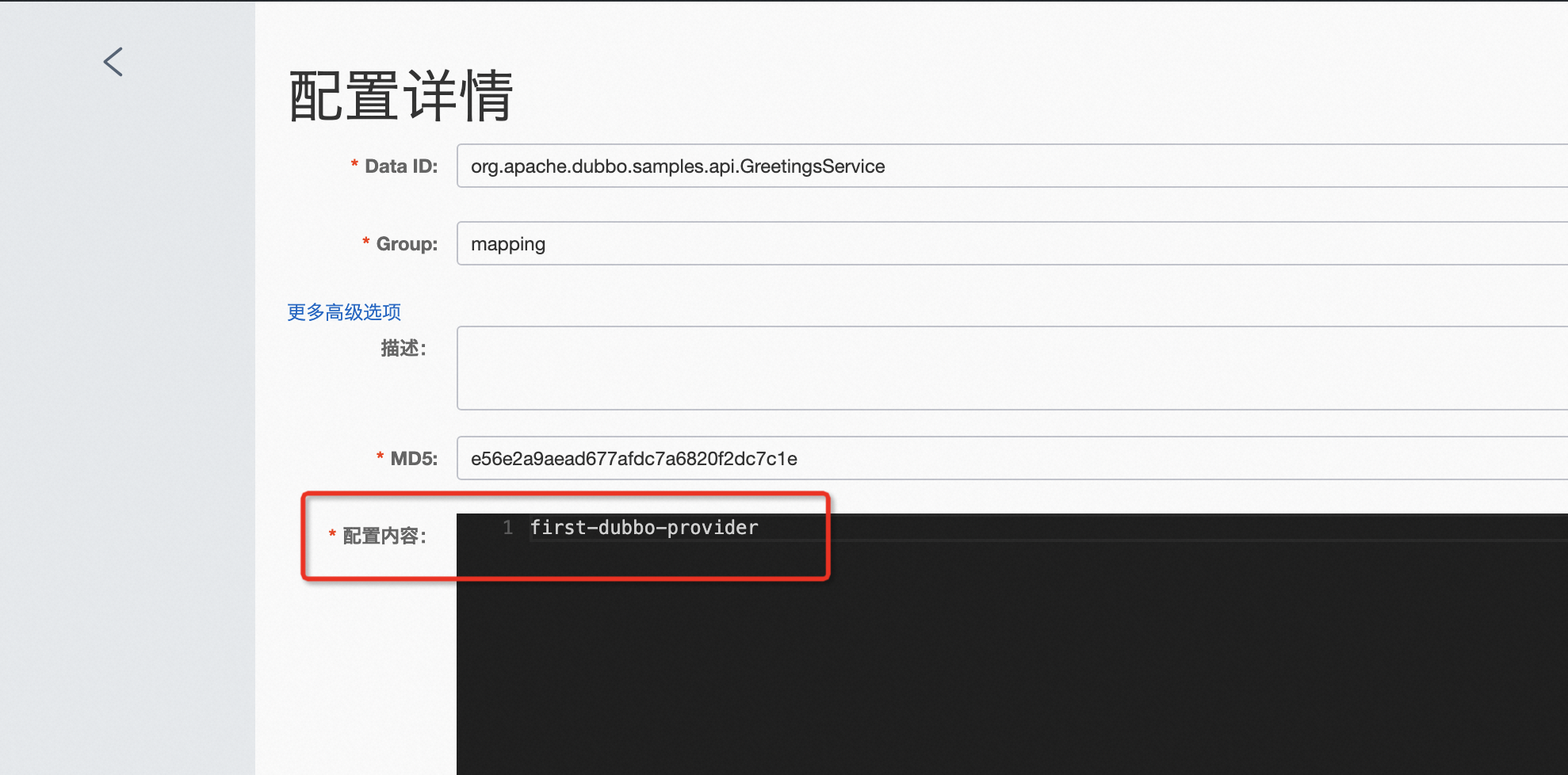
As shown above, check if the configuration includes the expected application name. If found, continue troubleshooting using this application name as the service name. If not found, move to Step 3 for troubleshooting.
After finding the application name, further query service information through “Service Management” - “Service List”, searching by service name.
Note: Here the service name is the application name queried from the previous step, not the interface name.
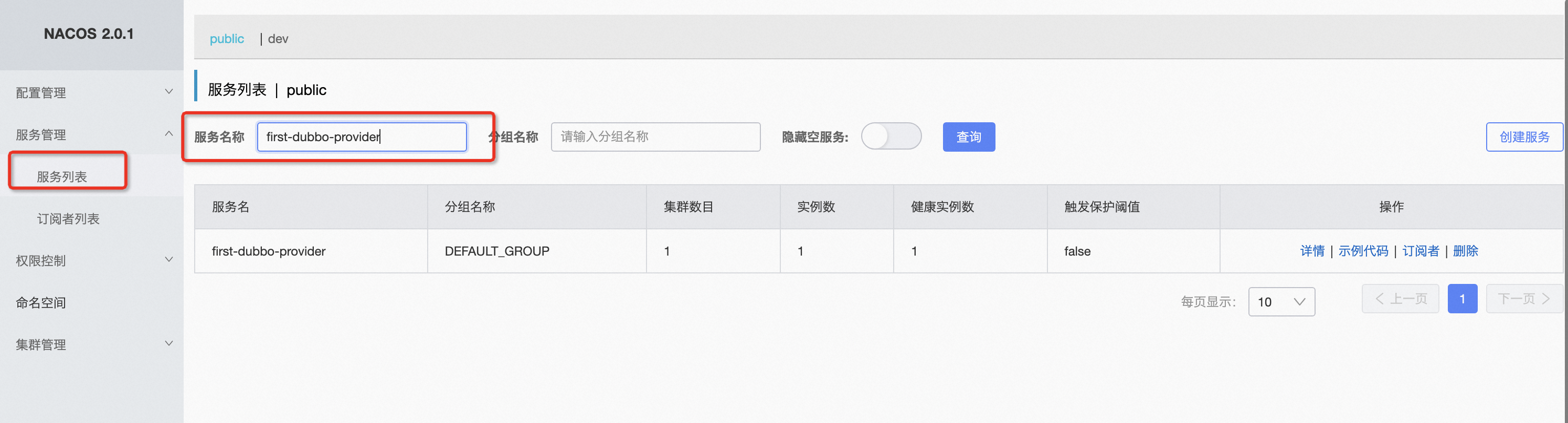
As shown above, please confirm whether you can find the expected service side based on the service discovery model established in Step 1. If found, proceed with Step x for further troubleshooting. If not found, move to Step 3 for troubleshooting.
2.2.2 Query through Zookeeper Registry
1)Interface level service discovery
In the interface-level service discovery model, you can directly query service information through the Zookeeper command line, with the path being /dubbo/${interfaceName}/providers.
Note: The interface name is used in the path on the Zookeeper registry, while group and version numbers are parameters in the address. If you specified the group’s or version’s parameters of the service, check each address parameter.
[zk: localhost:2181(CONNECTED) 1] ls /dubbo/org.apache.dubbo.samples.api.GreetingsService/providers
[dubbo%3A%2F%2F30.221.144.195%3A20880%2Forg.apache.dubbo.samples.api.GreetingsService%3Fanyhost%3Dtrue%26application%3Dfirst-dubbo-provider%26background%3Dfalse%26deprecated%3Dfalse%26dubbo%3D2.0.2%26dynamic%3Dtrue%26environment%3Dproduct%26executor-management-mode%3Ddefault%26file-cache%3Dtrue%26generic%3Dfalse%26interface%3Dorg.apache.dubbo.samples.api.GreetingsService%26methods%3DsayHi%26pid%3D37828%26prefer.serialization%3Dfastjson2%2Chessian2%26release%3D3.2.0-beta.6-SNAPSHOT%26service-name-mapping%3Dtrue%26side%3Dprovider%26timestamp%3D1677463548624]
As shown above, confirm whether you can query the expected service side based on the service discovery model established in Step 1. If found, proceed with Step x for further troubleshooting. If not found, move to Step 3 for troubleshooting.
2)Application level service discovery
In the application-level service discovery model, you first need to check the service mapping information, which can be queried through the Zookeeper command line with the path /dubbo/mapping/${interfaceName}.
Note: When checking service mapping, the interfaceName refers to the interface name, and no group or version needs to be specified.
[zk: localhost:2181(CONNECTED) 6] get /dubbo/mapping/org.apache.dubbo.samples.api.GreetingsService
first-dubbo-provider
As shown above, check if the configuration content contains the expected application name. If found, proceed with this application name to continue troubleshooting. If not found, move to Step 3 for troubleshooting.
After finding the application name, further query service information directly via the Zookeeper command line, with the path being /services/${interfaceName}.
Note: The service name here is the application name identified from the previous step, not the interface name.
[zk: localhost:2181(CONNECTED) 7] ls /services/first-dubbo-provider
[30.221.144.195:20880]
As shown above, confirm whether you can find the expected service side based on the service discovery model established in Step 1. If found, proceed with Step x for further troubleshooting. If not found, move to Step 3 for troubleshooting.
Note: If after utilizing the application-level service discovery model, you still cannot locate the consumer-side address, it may indicate that the service provider has not published the corresponding service; therefore, start troubleshooting from Step 3.
3 Check whether the service provider has published the service
3.1 Check through Dubbo QoS (recommended)
When Dubbo applications start, a QoS service is published by default on port 22222 locally, which can be used to query the status of nodes at runtime. Typically, if dubbo.application.qos-enable or dubbo.application.qos-port is not explicitly configured, you can use this method to check service information.
Find the machine expected to publish this service, log into its console, and execute telnet 127.0.0.1 22222 and ls:
➜ telnet 127.0.0.1 22222
Trying 127.0.0.1...
Connected to localhost.
Escape character is '^]'.
___ __ __ ___ ___ ____
/ _ \ / / / // _ ) / _ ) / __ \
/ // // /_/ // _ |/ _ |/ /_/ /
/____/ \____//____//____/ \____/
dubbo>ls
As Provider side:
+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+---------------------+
| Provider Service Name | PUB |
+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+---------------------+
| org.apache.dubbo.samples.api.GreetingsService |nacos-A(Y)/nacos-I(Y)|
+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+---------------------+
|DubboInternal - first-dubbo-provider/org.apache.dubbo.metadata.MetadataService:1.0.0| |
+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+---------------------+
As Consumer side:
+---------------------+---+
|Consumer Service Name|NUM|
+---------------------+---+
dubbo>
If telnet is not available on the machine, you can also use cURL to initiate a call, where the request address is http://127.0.0.1:22222/ls:
➜ curl http://127.0.0.1:22222/ls
As Provider side:
+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+---------------------+
| Provider Service Name | PUB |
+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+---------------------+
| org.apache.dubbo.samples.api.GreetingsService |nacos-A(Y)/nacos-I(Y)|
+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+---------------------+
|DubboInternal - first-dubbo-provider/org.apache.dubbo.metadata.MetadataService:1.0.0| |
+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+---------------------+
As Consumer side:
+---------------------+---+
|Consumer Service Name|NUM|
+---------------------+---+
Note: By default, the ls command only allows local calls. If you cannot log into the corresponding machine, refer to 3.2 to check via logs.
As shown in the results, check whether your published service name exists in the As Provider side column. If it does, it means the service has been published. The information in the second column, PUB, indicates the registration status of the service, formatted as ${registryName}-${registerType}(${status}). The registerType can be either A or I, representing application-level and interface-level service discovery models. This information can help determine the service publication status.
If you cannot find your published service, please check the following checklist:
- Has the service been added to the running code corresponding to the machine?
- Is the service properly configured in the Dubbo environment? Check if configurations like
@EnableDubbo,@DubboService, or XML are correct.
If you found your published service but its status is N, check the following checklist:
- Is the service configured with
register=false? - Was there an external command that invoked
offline? - Did the application start successfully (including but not limited to states of Tomcat, Spring)?
If you found your published service, but its corresponding service discovery model is erroneous, check the following checklist:
- Is the registry address configured with
registry-type=service? - Is the application-level registration model configured, such as
dubbo.application.register-type?
If you found your published service and its corresponding service discovery model status is Y, proceed to Step 4 for further troubleshooting.
3.2 Check through logs
If you cannot use Dubbo QoS for various reasons, search for [DUBBO] Export dubbo service ${serviceName} in the logs of the machine to check if the service has been published.
[26/02/23 04:34:41:041 CST] main INFO config.ServiceConfig: [DUBBO] Export dubbo service org.apache.dubbo.samples.api.GreetingsService to local registry url : injvm://***, dubbo version: 3.1.7, current host: 192.168.31.5
As shown above, this indicates that the service has been published. If you cannot find your published service, check the following checklist:
- Has the service been added to the running code corresponding to the machine?
- Is the service properly configured in the Dubbo environment? Verify configurations like
@EnableDubbo,@DubboService, or XML settings are accurate.
After confirming that the service has been published, search for [DUBBO] Register dubbo service ${serviceName} to registry ${registryAddress} in the logs of the corresponding machine to check if the service has been registered.
[26/02/23 04:34:41:041 CST] main INFO config.ServiceConfig: [DUBBO] Register dubbo service org.apache.dubbo.samples.api.GreetingsService url dubbo://*** to registry 127.0.0.1:8848, dubbo version: 3.1.7, current host: 192.168.31.5
As shown above, this indicates that the service has been registered. If you cannot find relevant logs, please check the following checklist:
- Is the service configured with
register=false? - Is there an external command that called
offline? - Did the application start successfully (including but not limited to states of Tomcat and Spring)?
If you found your registered service, proceed to Step 4 for further troubleshooting.
4 Check the service provider’s registry configuration
4.1 Check through Dubbo Admin (recommended)
Note: Supported in Dubbo version 3.2.0 and above.
When Dubbo applications start, a QoS service is published by default on port 22222 locally, which can be used to query node statuses at runtime. Typically, if dubbo.application.qos-enable or dubbo.application.qos-port was not explicitly configured, you can use this method to check service information.
Find the machine expected to publish this service, log into its console, and execute telnet 127.0.0.1 22222 and getConfig RegistryConfig:
➜ telnet 127.0.0.1 22222
Trying 127.0.0.1...
Connected to localhost.
Escape character is '^]'.
___ __ __ ___ ___ ____
/ _ \ / / / // _ ) / _ ) / __ \
/ // // /_/ // _ |/ _ |/ /_/ /
/____/ \____//____//____/ \____/
dubbo>getConfig RegistryConfig
ApplicationModel: Dubbo Application[1.1](first-dubbo-provider)
RegistryConfig: null
<dubbo:registry address="nacos://127.0.0.1:8848" protocol="nacos" port="8848" />
As shown in the above results, check whether the corresponding registry configuration meets expectations. If not, adjust the configuration accordingly. If checks for Step 3 and Step 4 both meet expectations, the service should be queryable in the registry outlined in Step 2. If it cannot be found, check whether the registry is functioning correctly.
Note: The getConfig command only allows local calls. If you cannot log into the corresponding machine, refer to 4.2 to check through logs.
4.2 Check through logs
If you cannot use Dubbo QoS for various reasons, search for [DUBBO] <dubbo:registry address= in the logs of the corresponding machine to check the registry configuration.
[27/02/23 09:36:46:046 CST] main INFO context.ConfigManager: [DUBBO] <dubbo:registry address="nacos://127.0.0.1:8848" protocol="nacos" port="8848" />, dubbo version: 3.2.0-beta.6-SNAPSHOT, current host: 30.221.144.195
As shown in the above results, please check whether the corresponding registry configuration meets expectations. If not, modify it accordingly. If checks for Step 3 and Step 4 both meet expectations, the service should be queryable in the registry outlined in Step 2. If it cannot be found, check the registry functionality’s status.
5 Check the service provider’s network configuration
Once the service has been published at the service provider, check whether the network firewall (iptables, ACL, etc.) allows communication on Dubbo ports. The default Dubbo protocol port number is 20880, while the Triple protocol port number is 50051. Specific port numbers can be obtained from the information in the registry outlined in Step 2.
Testing method: Use telnet directly on the consumption machine to reach the remote port.
6 Check whether the consumer has subscribed to the service
6.1 Check through Dubbo QoS (recommended)
When Dubbo applications start, a QoS service is published by default on port 22222 locally, allowing runtime queries of node status. Typically, if dubbo.application.qos-enable or dubbo.application.qos-port are not specifically configured, you can use this method to check service information.
Find the machine expected to publish this service, log into its console, and execute telnet 127.0.0.1 22222 and ls:
➜ telnet 127.0.0.1 22222
Trying 127.0.0.1...
Connected to localhost.
Escape character is '^]'.
___ __ __ ___ ___ ____
/ _ \ / / / // _ ) / _ ) / __ \
/ // // /_/ // _ |/ _ |/ /_/ /
/____/ \____//____//____/ \____/
dubbo>ls
As Provider side:
+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+---+
| Provider Service Name |PUB|
+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+---+
|DubboInternal - first-dubbo-consumer/org.apache.dubbo.metadata.MetadataService:1.0.0| |
+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+---+
As Consumer side:
+---------------------------------------------+---------------------+
| Consumer Service Name | NUM |
+---------------------------------------------+---------------------+
|org.apache.dubbo.samples.api.GreetingsService|zookeeper-AF(I-1,A-1)|
+---------------------------------------------+---------------------+
dubbo>
If telnet is not available on the machine, you can also initiate a call using cURL, where the request address is http://127.0.0.1:22222/ls:
➜ curl http://127.0.0.1:22222/ls
As Provider side:
+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+---+
| Provider Service Name |PUB|
+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+---+
|DubboInternal - first-dubbo-consumer/org.apache.dubbo.metadata.MetadataService:1.0.0| |
+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+---+
As Consumer side:
+---------------------------------------------+---------------------+
| Consumer Service Name | NUM |
+---------------------------------------------+---------------------+
|org.apache.dubbo.samples.api.GreetingsService|zookeeper-AF(I-1,A-1)|
+---------------------------------------------+---------------------+
Note: By default, the ls command only allows local calls. If you cannot log into the corresponding machine, refer to 3.2 for checks via logs.
As shown in the resulting output, check whether the service name you published exists in the As Consumer side column. If it does, it indicates the service has been published. The information in the second column, NUM, displays the registration status of the service formatted as ${registryName}-${migrationType}(${level}-${count}).
migrationTypecan be one of three types:AF,FA, andFI, indicating subscription modes.AFprioritizes addresses from the application-level model; if the application-level address is not found, it defaults to using the interface-level model’s address.FAandFIutilize only the application-level and interface-level addresses, respectively.levelcan beIorA, which indicate whether the address is from the interface-level model or the application-level model.
If you cannot locate your published service, please check the following checklist:
- Has the service been added to the corresponding running code on the machine?
- Is the service correctly configured in the Dubbo environment? Check configurations like
@EnableDubbo,@DubboReference, or XML for correctness.
If you found your published service, but the number of addresses is 0, please check:
- The working status of the registry.
- Reassess from Step 2.
If found with an incorrect service discovery model, check:
- The configured subscription migration rules in files like
dubbo-migration.yamlor dynamic configurations. Refer toApplication-level Service Discovery Address Migration Rules.
If you located your published service and the corresponding service discovery model shows more than 0 addresses, proceed to Step 7 for further troubleshooting.
6.2 Check through logs
If you cannot access Dubbo QoS for various reasons, search for [DUBBO] Subscribe: in the logs of the corresponding machine to verify if the service is subscribed.
[27/02/23 11:02:05:005 CST] main INFO zookeeper.ZookeeperRegistry: [DUBBO] Subscribe: consumer://***/org.apache.dubbo.samples.api.GreetingsService?***, dubbo version: 3.2.0-beta.6, current host: 30.221.144.195
If found, it indicates that the service has been published. If you cannot find your published service, please check the following checklist:
- Has the service been added to the corresponding running code on the machine?
- Is the service properly configured in the Dubbo environment? Verify configurations like
@EnableDubbo,@DubboReference, or XML settings for correctness.
After confirming that the service is subscribed, you can check the logs for [DUBBO] Received invokers changed event from registry. to assess if the service has been pushed.
[27/02/23 11:02:05:005 CST] main INFO integration.RegistryDirectory: [DUBBO] Received invokers changed event from registry. Registry type: interface. Service Key: org.apache.dubbo.samples.api.GreetingsService. Urls Size : 1. Invokers Size : 1. Available Size: 1. Available Invokers : 30.221.144.195:20880, dubbo version: 3.2.0-beta.6, current host: 30.221.144.195
If it is found, it indicates the service has been pushed. If you cannot locate the relevant logs, please check the following checklist:
- The working status of the registry.
- Reassess from Step 2.
If you found your registered service, proceed to Step 7 for further investigation.
Note: The push logs are only supported in version 3.2.0 and above.
7 Check the configuration of the consumer’s registry
Note: The troubleshooting thoughts in this section are similar to Step 4’s check on the service provider’s registry configuration.
7.1 Check through Dubbo Admin (recommended)
Note: Supported in Dubbo 3.2.0 and above.
When Dubbo applications start, a QoS service is published by default on port 22222 locally, which can be used to query node statuses at runtime. Typically, if dubbo.application.qos-enable or dubbo.application.qos-port are not explicitly configured, you can use this method to check service information.
Find the expected machine publishing this service, log into its console, and execute telnet 127.0.0.1 22222 and getConfig RegistryConfig:
➜ telnet 127.0.0.1 22222
Trying 127.0.0.1...
Connected to localhost.
Escape character is '^]'.
___ __ __ ___ ___ ____
/ _ \ / / / // _ ) / _ ) / __ \
/ // // /_/ // _ |/ _ |/ /_/ /
/____/ \____//____//____/ \____/
dubbo>getConfig RegistryConfig
ApplicationModel: Dubbo Application[1.1](first-dubbo-provider)
RegistryConfig: null
<dubbo:registry address="nacos://127.0.0.1:8848" protocol="nacos" port="8848" />
As shown in the above results, check whether the corresponding registry configuration meets expectations. If not, adjust the configuration accordingly. If checks for Step 6 and Step 7 both meet expectations, the service should be queryable in the registry outlined in Step 2. If it cannot be found, check whether the registry is functioning correctly.
Note: The getConfig command only allows local calls. If you cannot log into the corresponding machine, refer to 4.2 to check via logs.
7.2 Check through logs
If you cannot access Dubbo QoS for various reasons, search for [DUBBO] <dubbo:registry address= in the logs of the corresponding machine to verify the registry configuration.
[27/02/23 09:36:46:046 CST] main INFO context.ConfigManager: [DUBBO] <dubbo:registry address="nacos://127.0.0.1:8848" protocol="nacos" port="8848" />, dubbo version: 3.2.0-beta.6-SNAPSHOT, current host: 30.221.144.195
As shown in the above results, examine if the corresponding registry configuration meets expectations. If not, modify accordingly. If checks for Step 3 and Step 4 align with expectations, the service should be queryable in the registry outlined in Step 2. If it cannot be found, check the status of the registry’s functionality.
8 Check the address information pushed by the registry
Note: The query commands in this section are supported in Dubbo version 3.2.0 and above.
When Dubbo applications start, a QoS service is published by default on port 22222 locally, which can be used to query node statuses at runtime. Typically, if dubbo.application.qos-enable or dubbo.application.qos-port are not explicitly configured, you can use this method to check service information.
Find the expected machine publishing this service, log into its console, and execute telnet 127.0.0.1 22222 and getAddress ${serviceName}:
➜ telnet 127.0.0.1 22222
Trying 127.0.0.1...
Connected to localhost.
Escape character is '^]'.
___ __ __ ___ ___ ____
/ _ \ / / / // _ ) / _ ) / __ \
/ // // /_/ // _ |/ _ |/ /_/ /
/____/ \____//____//____/ \____/
dubbo>getAddress org.apache.dubbo.samples.api.GreetingsService
ConsumerModel: org.apache.dubbo.samples.api.GreetingsService@38b2d161
Registry: zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181/org.apache.dubbo.registry.RegistryService?application=first-dubbo-consumer&dubbo=2.0.2&environment=product&executor-management-mode=default&file-cache=true&interface=org.apache.dubbo.registry.RegistryService&pid=44482&release=3.2.0-beta.6-SNAPSHOT
MigrationStep: APPLICATION_FIRST
Interface-Level:
All Invokers:
dubbo://30.221.144.195:20880/org.apache.dubbo.samples.api.GreetingsService?anyhost=true&application=first-dubbo-provider&background=false&check=false&deprecated=false&dubbo=2.0.2&dynamic=true&executor-management-mode=default&file-cache=true&generic=false&interface=org.apache.dubbo.samples.api.GreetingsService&methods=sayHi&prefer.serialization=fastjson2,hessian2&release=3.2.0-beta.6-SNAPSHOT&service-name-mapping=true&side=provider
Valid Invokers:
dubbo://30.221.144.195:20880/org.apache.dubbo.samples.api.GreetingsService?anyhost=true&application=first-dubbo-provider&background=false&check=false&deprecated=false&dubbo=2.0.2&dynamic=true&executor-management-mode=default&file-cache=true&generic=false&interface=org.apache.dubbo.samples.api.GreetingsService&methods=sayHi&prefer.serialization=fastjson2,hessian2&release=3.2.0-beta.6-SNAPSHOT&service-name-mapping=true&side=provider
Disabled Invokers:
Application-Level:
All Invokers:
dubbo://30.221.144.195:20880/org.apache.dubbo.samples.api.GreetingsService?anyhost=true&application=first-dubbo-consumer&background=false&deprecated=false&dubbo=2.0.2&dubbo.endpoints=[{"port":20880,"protocol":"dubbo"}]&dubbo.metadata-service.url-params={"prefer.serialization":"fastjson2,hessian2","version":"1.0.0","dubbo":"2.0.2","release":"3.2.0-beta.6-SNAPSHOT","side":"provider","port":"20880","protocol":"dubbo"}&dubbo.metadata.revision=e37fc5748b33c325056556550d33dde7&dubbo.metadata.storage-type=local&dynamic=true&environment=product&executor-management-mode=default&file-cache=true&generic=false&interface=org.apache.dubbo.samples.api.GreetingsService&methods=sayHi&pid=44482&prefer.serialization=fastjson2,hessian2®ister.ip=30.221.144.195&release=3.2.0-beta.6-SNAPSHOT&service-name-mapping=true&side=consumer&sticky=false×tamp=1677466879396&unloadClusterRelated=false
Valid Invokers:
dubbo://30.221.144.195:20880/org.apache.dubbo.samples.api.GreetingsService?anyhost=true&application=first-dubbo-consumer&background=false&deprecated=false&dubbo=2.0.2&dubbo.endpoints=[{"port":20880,"protocol":"dubbo"}]&dubbo.metadata-service.url-params={"prefer.serialization":"fastjson2,hessian2","version":"1.0.0","dubbo":"2.0.2","release":"3.2.0-beta.6-SNAPSHOT","side":"provider","port":"20880","protocol":"dubbo"}&dubbo.metadata.revision=e37fc5748b33c325056556550d33dde7&dubbo.metadata.storage-type=local&dynamic=true&environment=product&executor-management-mode=default&file-cache=true&generic=false&interface=org.apache.dubbo.samples.api.GreetingsService&methods=sayHi&pid=44482&prefer.serialization=fastjson2,hessian2®ister.ip=30.221.144.195&release=3.2.0-beta.6-SNAPSHOT&service-name-mapping=true&side=consumer&sticky=false×tamp=1677466879396&unloadClusterRelated=false
Disabled Invokers:
dubbo>
As shown in the results above, the format is as follows:
ConsumerModel: Subscription information
Registry: Registry address
MigrationStep: Migration model (FORCE_APPLICATION, APPLICATION_FIRST, FORCE_INTERFACE)
Interface-Level: Address from the interface-level service discovery model
All Invokers:
All addresses pushed from the registry
Valid Invokers:
All available addresses
Disabled Invokers:
All blacklisted addresses (typically taken offline voluntarily)
Application-Level: Addresses from the application-level service discovery model
All Invokers:
All addresses pushed from the registry
Valid Invokers:
All available addresses
Disabled Invokers:
All blacklisted addresses (typically taken offline voluntarily)
Check whether the corresponding migration model meets your expectations, with the default being APPLICATION_FIRST. If the corresponding service discovery model is incorrect, please check the following checklist:
- The configured subscription migration rule, in files like
dubbo-migration.yamlor dynamic settings. Refer toApplication-level Service Discovery Address Migration Rules
If the migration model is correct, confirm that all addresses in the corresponding model match expectations. If not, check the following checklist:
- The working status of the registry
- Reassess from Step 2
If the addresses pushed by the registry meet your expectations, check whether the available addresses match expectations. If they do not, it is usually due to connection issues leading to blacklisting, often appearing under conditions like failures in tier-4 networking or room outages. Please proceed to Step 9 for further investigation.
If the available addresses are as expected, proceed to Step 10 for inspection.
Note: The getAddress command only allows local calls.
9 Check the network connectivity between the consumer and service provider
After the service provider has published the service, ensure that the network firewall (iptables, ACLs, etc.) allows communication on Dubbo ports. The default Dubbo protocol port is 20880, and the Triple protocol port is 50051. Specific port numbers can be obtained from the registry information found in Step 2.
Testing method: On the consumer-side machine, use telnet directly to ping the remote port.
Common exceptional scenarios:
- Multi-cluster deployments on both provider and consumer ends, but the underlying network is not connected.
- Production and testing share a registry, but the testing environment cannot call production services (Dubbo highly discourages mixing testing and production environments).
- Debugging on a single machine, but the network is not connected to the broader test network.
- Network outages causing node disconnections.
- Tier-4 network ACL rules not permitting access to Dubbo ports.
- Poor network quality, service provider overload, or similar conditions impacting connection quality.
10 Check routing information
Note: Supported in Dubbo version 3.1.0 and above.
10.1 Check logs during errors
When Dubbo encounters invocation exceptions, you can search for [DUBBO] No provider available after the route for the service in the machine’s logs to review the routing status.
[27/02/23 11:33:16:016 CST] main WARN cluster.SingleRouterChain: [DUBBO] No provider available after the route for the service org.apache.dubbo.samples.api.GreetingsService from registry 30.221.144.195 on the consumer 30.221.144.195 using the dubbo version 3.2.0-beta.6-SNAPSHOT. Router snapshot is below:
[ Parent (Input: 1) (Current Node Output: 1) (Chain Node Output: 0) ] Input: 30.221.144.195:20880 -> Chain Node Output: Empty
[ MockInvokersSelector (Input: 1) (Current Node Output: 1) (Chain Node Output: 0) Router message: invocation.need.mock not set. Return normal Invokers. ] Current Node Output: 30.221.144.195:20880
[ StandardMeshRuleRouter (Input: 1) (Current Node Output: 1) (Chain Node Output: 0) Router message: MeshRuleCache has not been built. Skip route. ] Current Node Output: 30.221.144.195:20880
[ TagStateRouter (Input: 1) (Current Node Output: 0) (Chain Node Output: 0) Router message: Disable Tag Router. Reason: tagRouterRule is invalid or disabled ] Current Node Output: Empty, dubbo version: 3.2.0-beta.6-SNAPSHOT, current host: 30.221.144.195, error code: 2-2. This may be caused by No provider available after route for the service, go to https://dubbo.apache.org/faq/2/2 to find instructions
Check the log line where Current Node Output: 0 appears; this usually indicates the addresses are empty as a result of routing at that level.
10.2 Sampling Query through Dubbo Admin
For machines operating online, Dubbo offers the ability to dynamically sample routing results, which can be enabled via Dubbo QoS.
To turn on sampling:
dubbo>enableRouterSnapshot com.dubbo.*
OK. Found service count: 1. This will cause performance degradation, please be careful!
dubbo>
To obtain the sample results:
dubbo>getRecentRouterSnapshot
1658224330156 - Router snapshot service com.dubbo.dubbointegration.BackendService from registry 172.18.111.184 on the consumer 172.18.111.184 using the dubbo version 3.0.9 is below:
[ Parent (Input: 2) (Current Node Output: 2) (Chain Node Output: 2) ] Input: 172.18.111.187:20880,172.18.111.183:20880 -> Chain Node Output: 172.18.111.187:20880,172.18.111.183:20880
[ MockInvokersSelector (Input: 2) (Current Node Output: 2) (Chain Node Output: 2) Router message: invocation.need.mock not set. Return normal Invokers. ] Current Node Output: 172.18.111.187:20880,172.18.111.183:20880
[ StandardMeshRuleRouter (Input: 2) (Current Node Output: 2) (Chain Node Output: 2) Router message: MeshRuleCache has not been built. Skip route. ] Current Node Output: 172.18.111.187:20880,172.18.111.183:20880
[ TagStateRouter (Input: 2) (Current Node Output: 2) (Chain Node Output: 2) Router message: Disable Tag Router. Reason: tagRouterRule is invalid or disabled ] Current Node Output: 172.18.111.187:20880,172.18.111.183:20880
[ ServiceStateRouter (Input: 2) (Current Node Output: 2) (Chain Node Output: 2) Router message: Directly return. Reason: Invokers from previous router is empty or conditionRouters is empty. ] Current Node Output: 172.18.111.187:20880,172.18.111.183:20880
[ AppStateRouter (Input: 2) (Current Node Output: 2) (Chain Node Output: 2) Router message: Directly return. Reason: Invokers from previous router is empty or conditionRouters is empty. ] Current Node Output: 172.18.111.187:20880,172.18.111.183:20880
1658224330156 - Router snapshot service com.dubbo.dubbointegration.BackendService from registry 172.18.111.184 on the consumer 172.18.111.184 using the dubbo version 3.0.9 is below:
[ Parent (Input: 2) (Current Node Output: 2) (Chain Node Output: 2) ] Input: 172.18.111.187:20880,172.18.111.183:20880 -> Chain Node Output: 172.18.111.187:20880,172.18.111.183:20880
[ MockInvokersSelector (Input: 2) (Current Node Output: 2) (Chain Node Output: 2) Router message: invocation.need.mock not set. Return normal Invokers. ] Current Node Output: 172.18.111.187:20880,172.18.111.183:20880
[ StandardMeshRuleRouter (Input: 2) (Current Node Output: 2) (Chain Node Output: 2) Router message: MeshRuleCache has not been built. Skip route. ] Current Node Output: 172.18.111.187:20880,172.18.111.183:20880
[ TagStateRouter (Input: 2) (Current Node Output: 2) (Chain Node Output: 2) Router message: Disable Tag Router. Reason: tagRouterRule is invalid or disabled ] Current Node Output: 172.18.111.187:20880,172.18.111.183:20880
[ ServiceStateRouter (Input: 2) (Current Node Output: 2) (Chain Node Output: 2) Router message: Directly return. Reason: Invokers from previous router is empty or conditionRouters is empty. ] Current Node Output: 172.18.111.187:20880,172.18.111.183:20880
[ AppStateRouter (Input: 2) (Current Node Output: 2) (Chain Node Output: 2) Router message: Directly return. Reason: Invokers from previous router is empty or conditionRouters is empty. ] Current Node Output: 172.18.111.187:20880,172.18.111.183:20880
···
dubbo>
To disable sampling:
dubbo>disableRouterSnapshot com.dubbo.*
OK. Found service count: 1
dubbo>
Note: Collecting routing information will consume some performance, so kindly ensure to disable it promptly after troubleshooting is complete. Reference document: Routing State Commands