Port Protocol Multiplexing
Feature description
By configuring the protocol, dubbo3 can support port protocol multiplexing. For example, after using the Triple protocol to enable port multiplexing, you can add Dubbo protocol support, and Qos protocol support. These protocols are identified by a unified port multiplexing It can be used for service protocol migration, which is processed by the server, and can save ports and related resources and reduce the complexity of operation and maintenance.
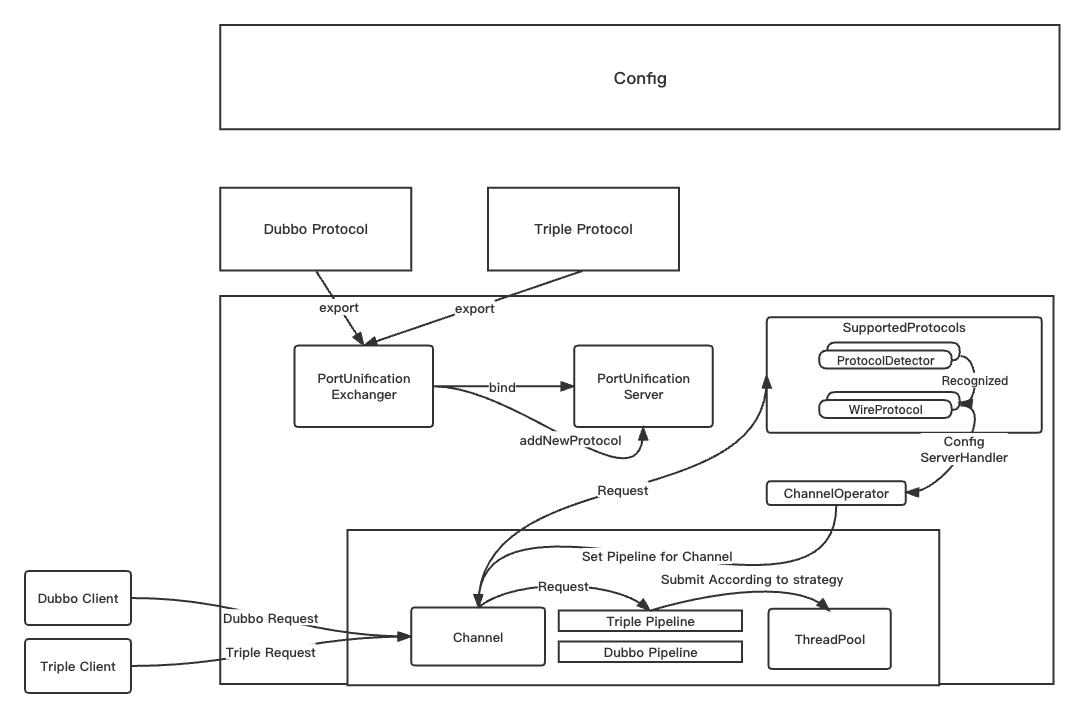
In the service creation phase, different Protocol objects are created for export by obtaining the protocol configuration exported by the service from the Config layer. in the process of exporting In , if it is not the first time to create a server with port multiplexing, the Exchanger will save the data passed by the protocol layer to the server for subsequent processing of messages of this protocol type.
When the client’s message is delivered, it will first be passed to the ProtocolDetector through the server. If the identification is completed, the client will be marked as the corresponding protocol. And configure the corresponding processing logic through WireProtocol, and finally hand it over to ChannelOperator to complete the binding of the underlying IO framework and the processing logic of the corresponding Dubbo framework.
After the above protocol identification is completed, the Channel has determined how to process the remote client message, and it can be processed through the corresponding ServerPipeline (the processing thread of the message will also be determined according to the configuration information during the processing).
Reference use case
[https://github.com/apache/dubbo-samples/tree/master/dubbo-samples-port-unification](https://github.com/apache/dubbo-samples/tree/master/3-extensions/ protocol/dubbo-samples-port-unification)
configuration method
For the configuration method supported by Dubbo, please refer to Configuration Instructions
Service multi-protocol export
The ext-protocol parameter supports configuring multiple different protocols, and the protocols are separated by “,”.
xml configuration
<dubbo:protocol name="dubbo" port="-1" ext-protocol="tri,"/>
<bean id="greetingService" class="org.apache.dubbo.demo.provider.GreetingServiceImpl"/>
<dubbo:service delay="5000" version="1.0.0" group="greeting" timeout="5000" interface="org.apache.dubbo.demo.GreetingService" ref="greetingService" protocol="dubbo"/ >
API configuration
ProtocolConfig config = new ProtocolConfig(CommonConstants.TRIPLE, -1);
config.setExtProtocol(CommonConstants.DUBBO+",");
yaml configuration
dubbo:
application:
name: dubbo-springboot-demo-provider
protocol:
name: tri
port: -1
ext-protocol: dubbo,
properties configuration
dubbo.protocol.name=tri
dubbo.protocol.ext-protocol=dubbo,
dubbo.protocol.port=20880
Qos access
Qos module import
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.dubbo</groupId>
<artifactId>dubbo-qos</artifactId>
</dependency>
After importing the Qos module, related configuration items can be configured by referring to Qos Operation Manual .
By default, the Qos service based on port multiplexing is started after the module is imported.
How to use
Qos used
When the Qos protocol is connected to the port multiplexing scenario, after the connection is established, the client needs to send a message to the server first. Compared with the Qos protocol that provides services through a single port, the port multiplexing version of the Qos protocol handles the telnet connection. In some cases, the user needs to perform some operations to complete the protocol identification (choose one of the two).
Call the command directly
The recognition can also be completed by directly calling the commands supported by telnet. If the user is not familiar with it, the help command can be called to complete the recognition.
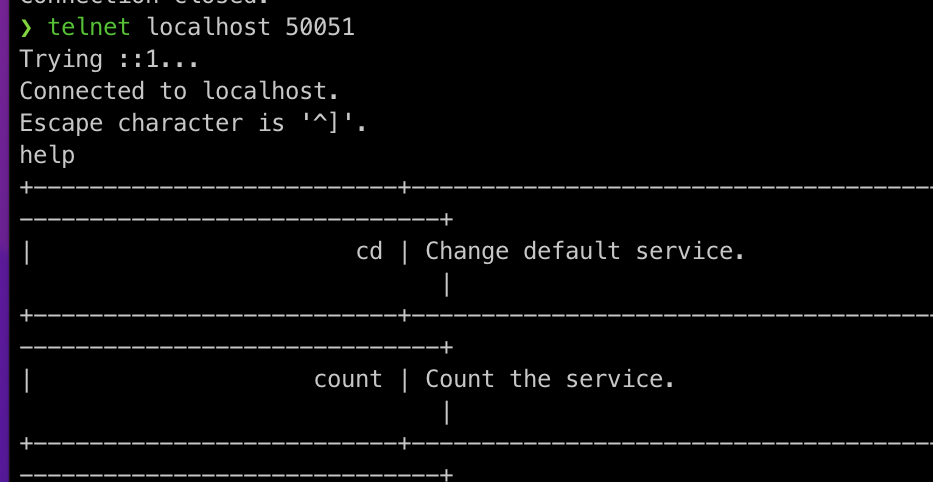
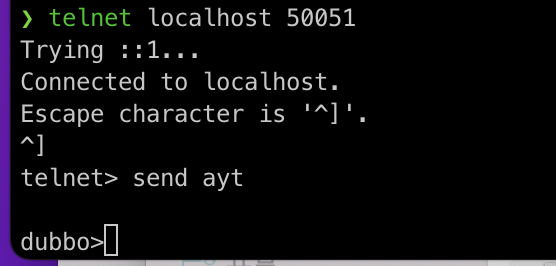
Send telnet command to identify
After establishing a connection through the telnet command, perform the following steps:
- Use crtl + “]” to enter the telnet interactive interface (telnet default escape character)
- Call “send ayt” to send a special identification field to the server (a special field of the telnet protocol)
- Press Enter to complete the message sending and enter the interactive interface of dubbo
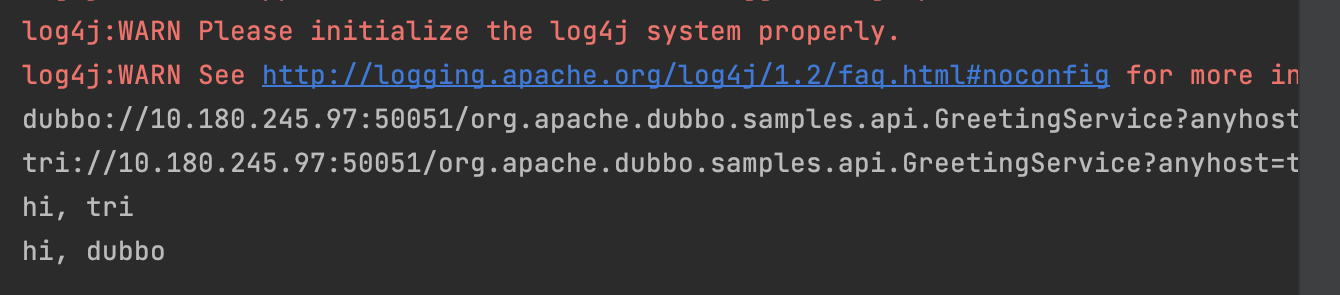
Service reference
Based on the example in dubbo-samples-port-unification, quote The configuration of services of different protocols and non-port multiplexing is consistent. Next, the URL information in the calling process is output through the InvokerListener on the Consumer side.
ReferenceConfig<GreetingService> reference = new ReferenceConfig<>();
reference.setInterface(GreetingService.class);
reference.setListener("consumer");
reference.setProtocol(this.protocol);
// reference.setProtocol(CommonConstants.DUBBO);
// reference.setProtocol(CommonConstants.TRIPLE);