Service Registration Discovery
1. Dubbo’s registration center
The registration center is responsible for saving the information of the server application in the RPC scenario.
The server registers the interface information and sends its own address to the registration center, and the client reads and subscribes to the list of addresses that need to be called from the registration center. The entire structure is shown in the figure:
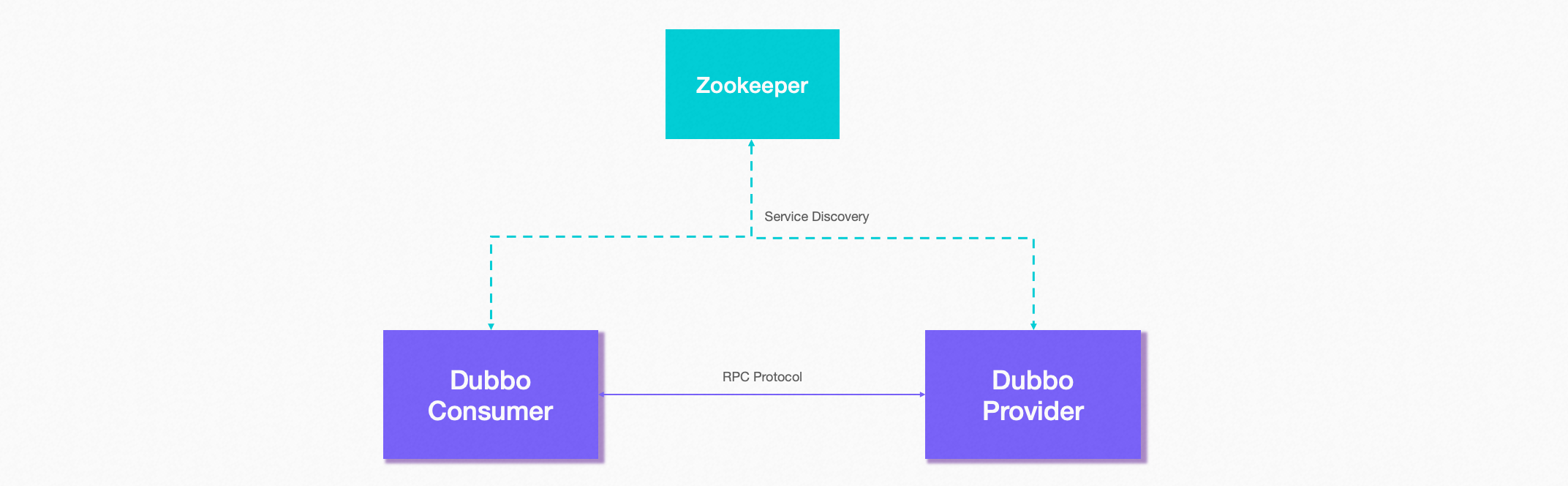
For details about Dubbo service discovery, please refer to Dubbo Official Website Concept Introduction
2. Service discovery concept
In the Dubbo ecosystem, service discovery has the following main concepts:
Application Application
The application is a dubbo service process, corresponding to an application name.
interface (service)
An interface is an RPC interface class, such as a Service defined by proto, or a Java Interface class. A dubbo process can contain multiple services/interfaces.
method
Methods are defined in interfaces, and an interface can contain multiple methods.
parameter list
The parameter list is defined in the method. Since Java supports overloading, a method can contain multiple parameter lists. For Go it is a one-to-one relationship.
registration message
In the “interface-level service discovery” scenario, the registration information mainly includes the application name, interface list, metadata information, and the IP address of the server. It is stored in the registration center in the form of URL for the client to query before initiating a call.
In the “application-level service discovery” scenario, the registration information only includes a small amount of application-level information such as the application name and the mapping from the application name to the interface, and the interface-level information is stored as metadata in the metadata center.
metadata
Metadata refers to interface information, such as interface name, contained methods, parameters corresponding to methods, serialization methods, protocols, and other information.
Registry
The registration center is used to save the information of the server.
Metadata center
The metadata center is used to save the metadata information of the server, and in the “application-level service discovery” scenario, it serves as the dependency of the “service introspection” stage.
Dubbo-go’s most advanced service grid capability introduces the following concepts
CPU name
The host name currently applies to the Service name registered on k8s. Other applications can access this application instance through the hostname.
endpoint
Endpoints include the instance’s IP address, port.
cluster
The cluster ID holds the data from {hostname, cluster_subset_name, port}
A cluster maintains a mapping of cluster IDs to all of its contained endpoints.
Service Mesh Metadata
The service mesh metadata is an interface name-to-hostname-to-map, which is used by clients to query the hostname information of the desired interface.
3. Dubbo-go Registration Center
The registry types supported by Dubbo-go are as follows:
| registry | registry name (for configuration) |
|---|---|
| Zookeeper | zookeeper |
| Nacos | nacos |
| Etcd | etcd |
| Consul | consul |
Related reading: [Analysis of application-level service discovery]