This article is more than one year old. Older articles may contain outdated content. Check that the information in the page has not become incorrect since its publication.
Apache Dubbo's First Node.js 3.0-alpha Version Officially Released
About Apache Dubbo3
Apache Dubbo is an easy-to-use, high-performance WEB and RPC framework, providing capabilities, tools, and best practices for creating enterprise-level microservices including service discovery, traffic governance, observability, and authentication. After several years of development, Dubbo3 has been widely promoted across Alibaba Group’s business lines, successfully replacing the HSF framework that had been in operation for years; meanwhile, the multi-language ecosystem of Dubbo3 has also developed rapidly, currently covering:
- apache/dubbo (java)
- apache/dubbo-go
- apache/dubbo-js (web, node.js)
- apache/dubbo-rust
Based on the Triple protocol defined by Dubbo3, you can easily write RPC services compatible with browsers, mobile, and gRPC, and run these services simultaneously on HTTP/1 and HTTP/2. The Dubbo Node.js SDK supports defining services using IDL or language-specific methods and provides a lightweight API for publishing or invoking these services.
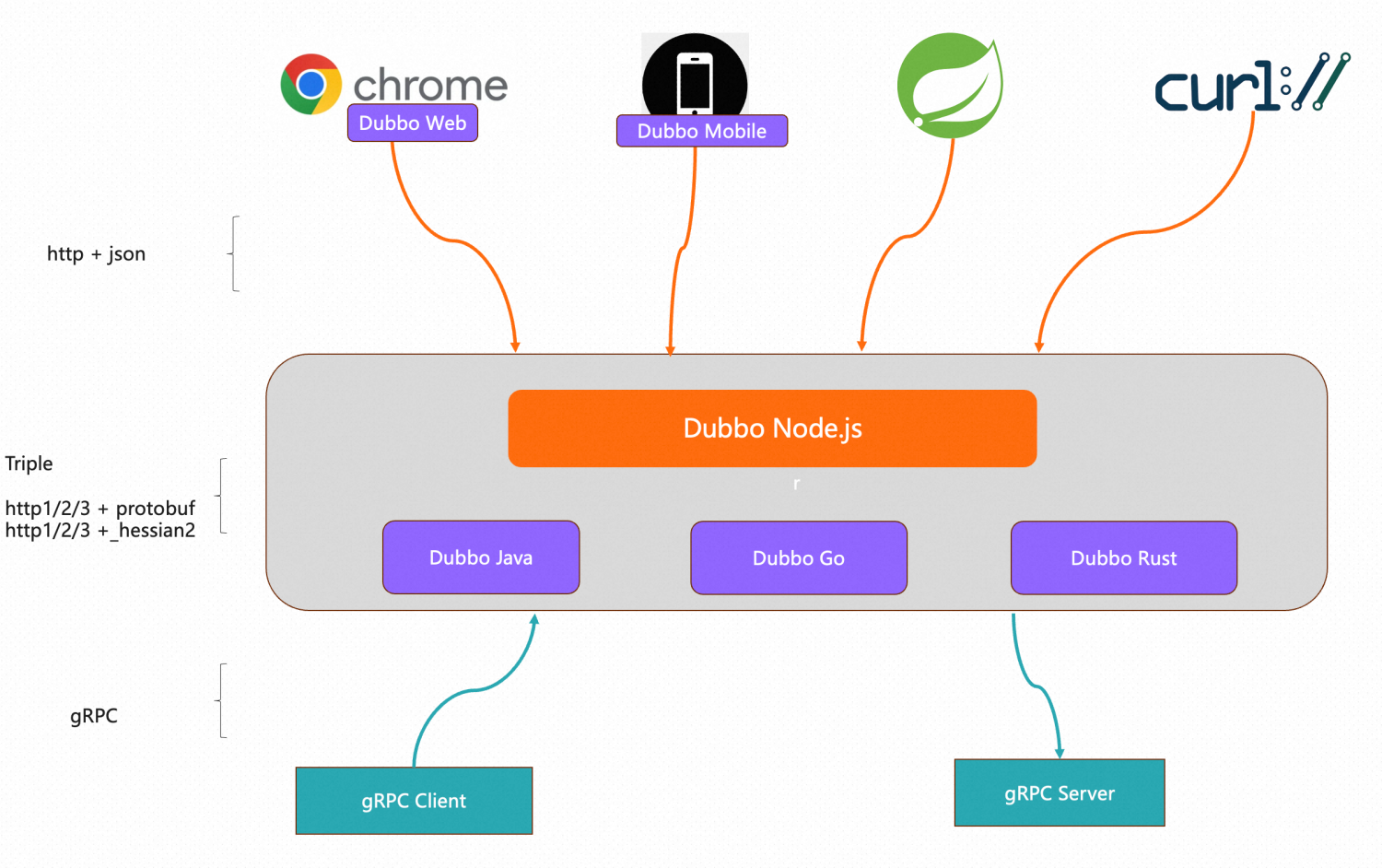
About the First Release of Dubbo3 Node.js
The dubbo-js project just released its first alpha version supporting the Dubbo3 protocol in September. This project is a Typescript version of Dubbo3, providing both Web and Node.js packages. The Web framework allows developers to access back-end services directly from the browser, while Node.js further enriches the choice of backend microservice technology stack. The current Node.js version primarily implements complete support for the Triple protocol, and the community will continue to enhance service governance capabilities such as address discovery and load balancing in future releases. The dubbo-js project is rapidly developing; developers interested in participating in the apache/dubbo-js project are welcome to search for DingTalk group: 29775027779 to join the developer group.
Complete Example of Node.js Microservice Development
This example is based on the latest released Node.js version, demonstrating RPC communication mode based on the Triple protocol, using Protocol Buffer to define RPC services, and demonstrating processes such as code generation, service publishing, and service access.
Prerequisites
Because of the use of Protocol Buffer, we first need to install the relevant code generation tools, including @bufbuild/protoc-gen-es, @bufbuild/protobuf, @apachedubbo/protoc-gen-apache-dubbo-es, @apachedubbo/dubbo.
npm install @bufbuild/protoc-gen-es @bufbuild/protobuf @apachedubbo/protoc-gen-apache-dubbo-es @apachedubbo/dubbo
Define Service
Now, use Protocol Buffer (IDL) to define a Dubbo service.
Create a directory and generate the file.
mkdir -p proto && touch proto/example.proto
Write the content.
syntax = "proto3";
package apache.dubbo.demo.example.v1;
message SayRequest {
string sentence = 1;
}
message SayResponse {
string sentence = 1;
}
service ExampleService {
rpc Say(SayRequest) returns (SayResponse) {}
}
This file declares a service called ExampleService, defining the Say method as well as its request parameter SayRequest and return value SayResponse.
Generate Code
Create the gen directory as the target directory for generated files.
mkdir -p gen
Run the following command to generate code files in the gen directory.
PATH=$PATH:$(pwd)/node_modules/.bin \
protoc -I proto \
--es_out gen \
--es_opt target=ts \
--apache-dubbo-es_out gen \
--apache-dubbo-es_opt target=ts \
example.proto
After running the command, you should see the following generated files in the target directory:
├── gen
│ ├── example_dubbo.ts
│ └── example_pb.ts
├── proto
│ └── example.proto
Implement Service
Next, we need to add business logic to implement ExampleService and register it with DubboRouter.
Create a dubbo.ts file.
import { DubboRouter } from "@apachedubbo/dubbo";
import { ExampleService } from "./gen/example_dubbo";
export default (router: DubboRouter) =>
// registers apache.dubbo.demo.example.v1
router.service(ExampleService, {
// implements rpc Say
async say(req) {
return {
sentence: `You said: ${req.sentence}`,
};
},
}, { serviceGroup: 'dubbo', serviceVersion: '1.0.0' });
Start Server
Dubbo services can be embedded into ordinary Node.js servers, Next.js, Express, or Fastify. Here we will use Fastify, so let’s install Fastify and the plugin we prepared for Fastify.
npm install fastify @apachedubbo/dubbo-fastify
Create a server.ts file, create a Server, and register the ExampleService implemented in the previous step. You can then directly initialize and start the Server, which will listen for requests on the specified port.
import { fastify } from "fastify";
import { fastifyDubboPlugin } from "@apachedubbo/dubbo-fastify";
import routes from "./dubbo";
async function main() {
const server = fastify();
await server.register(fastifyDubboPlugin, {
routes,
});
server.get("/", (_, reply) => {
reply.type("text/plain");
reply.send("Hello World!");
});
await server.listen({ host: "localhost", port: 8080 });
console.log("server is listening at", server.addresses());
}
void main();
Finally, run the code to start the service.
npx tsx server.ts
Access Service
The simplest way to access the service is using an HTTP/1.1 POST request, with parameters passed in standard JSON format as the HTTP payload. Below is an example of accessing using the cURL command:
curl \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--header 'TRI-Service-Version: 1.0.0' \
--header 'TRI-Service-group: dubbo' \
--data '{"sentence": "Hello World"}' \
http://localhost:8080/apache.dubbo.demo.example.v1.ExampleService/Say
You can also use a standard Dubbo client to request the service. We first need to get the service proxy from the generated code in the dubbo-node package, specify the server address, and initialize it; after that, we can initiate RPC calls.
Create a client.ts file.
import { createPromiseClient } from "@apachedubbo/dubbo";
import { ExampleService } from "./gen/example_dubbo";
import { createDubboTransport } from "@apachedubbo/dubbo-node";
const transport = createDubboTransport({
baseUrl: "http://localhost:8080",
httpVersion: "1.1",
});
async function main() {
const client = createPromiseClient(ExampleService, transport, { serviceVersion: '1.0.0', serviceGroup: 'dubbo' });
const res = await client.say({ sentence: "Hello World" });
console.log(res);
}
void main();
Run the client.
npx tsx client.ts
Summary
The current Node.js version primarily implements complete support for the Triple protocol. In future versions, the community will continue to enhance service governance capabilities such as address discovery and load balancing. The dubbo-js project is rapidly developing; developers interested in participating in the apache/dubbo-js project are welcome to search for the DingTalk group: 29775027779 to join the developer group.