Configuration Loading Process
This document focuses on how the Dubbo framework collects the required configuration (including application configuration, registry configuration, service configuration, etc.) during the application startup phase to complete the process of service exposure and reference.
Depending on how you drive it (such as Spring or naked API programming), the configuration form will certainly vary, for detail please refer to XML Configuration, Annotation Configuration and API Configuration. In addition to the differences in peripheral drivers, Dubbo’s configuration reads generally follow the following principles:
- Dubbo supports multiple levels of configuration and automatically override configurations according to predetermined priorities. Eventually, all configurations are aggregated to the data bus URL to drive subsequent service exposure, reference and other processes.
- ApplicationConfig, ServiceConfig and ReferenceConfig can be regarded as configuration sources, which collect configuration by directly user-oriented programming.
- The configuration format is mainly
Properties, and the configuration content follows conventions - The configuration format is mainly Properties, and the configuration content follows the agreed
path-basednaming [specification](#Configuration Format).
Configuration Source
First, starting with the configuration sources that Dubbo supports, there are four default configuration sources:
- JVM System Properties,-Dproperty
- Externalized Configuration
- ServiceConfig, ReferenceConfig and other programming interface collected configuration
- Local configuration file dubbo.properties
Override Priority
The figure below shows the priority of configuration override, decreasing from top to bottom:
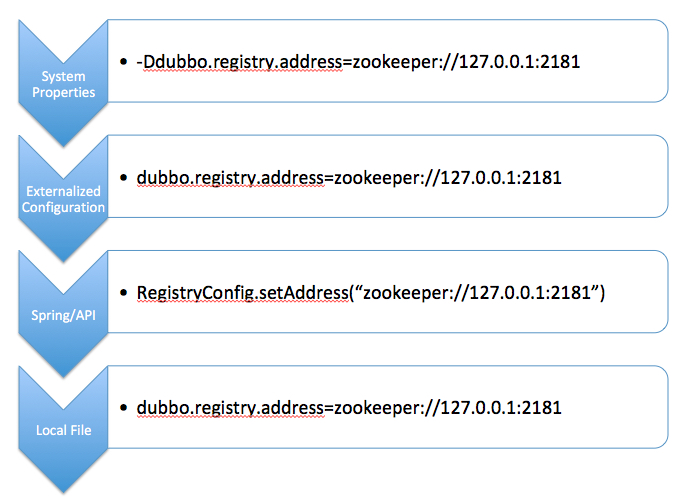
click here to view Externalize configuration details
Configuration Format
Currently, all configurations supported by Dubbo are in the format of .properties, including -D, Externalized Configuration, etc., and all configuration items in .properties follow a path-based Configuration format:
# Application level
dubbo.{config-type}[.{config-id}].{config-item}={config-item-value}
# Service level
dubbo.service.{interface-name}[.{method-name}].{config-item}={config-item-value}
dubbo.reference.{interface-name}[.{method-name}].{config-item}={config-item-value}
# Multiple configuration items
dubbo.{config-type}s.{config-id}.{config-item}={config-item-value}
- Application level
dubbo.application.name=demo-provider
dubbo.registry.address=zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181
dubbo.protocol.port=-1
- Service level
dubbo.service.org.apache.dubbo.samples.api.DemoService.timeout=5000
dubbo.reference.org.apache.dubbo.samples.api.DemoService.timeout=6000
dubbo.reference.org.apache.dubbo.samples.api.DemoService.sayHello.timeout=7000
- Multiple configuration items
dubbo.registries.unit1.address=zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181
dubbo.registries.unit2.address=zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2182
dubbo.protocols.dubbo.name=dubbo
dubbo.protocols.dubbo.port=20880
dubbo.protocols.hessian.name=hessian
dubbo.protocols.hessian.port=8089
- Extended configuration
dubbo.application.parameters.item1=value1
dubbo.application.parameters.item2=value2
dubbo.registry.parameters.item3=value3
dubbo.reference.org.apache.dubbo.samples.api.DemoService.parameters.item4=value4
Several programming approaches of configuration
Next, let’s look at the changes corresponding to ServiceConfig, ReferenceConfig and other programming interface collected configuration when selecting different development methods.
Spring
- XML
Refer to the sample
<!-- dubbo-provier.xml -->
<dubbo:application name="demo-provider"/>
<dubbo:config-center address="zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181"/>
<dubbo:registry address="zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181" simplified="true"/>
<dubbo:metadata-report address="redis://127.0.0.1:6379"/>
<dubbo:protocol name="dubbo" port="20880"/>
<bean id="demoService" class="org.apache.dubbo.samples.basic.impl.DemoServiceImpl"/>
<dubbo:service interface="org.apache.dubbo.samples.basic.api.DemoService" ref="demoService"/>
- Annotation
Refer to the sample
// AnnotationService implementation
@Service
public class AnnotationServiceImpl implements AnnotationService {
@Override
public String sayHello(String name) {
System.out.println("async provider received: " + name);
return "annotation: hello, " + name;
}
}
## dubbo.properties
dubbo.application.name=annotation-provider
dubbo.registry.address=zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181
dubbo.protocol.name=dubbo
dubbo.protocol.port=20880
- Spring Boot
Refer to the sample
## application.properties
# Spring boot application
spring.application.name=dubbo-externalized-configuration-provider-sample
# Base packages to scan Dubbo Component: @com.alibaba.dubbo.config.annotation.Service
dubbo.scan.base-packages=com.alibaba.boot.dubbo.demo.provider.service
# Dubbo Application
## The default value of dubbo.application.name is ${spring.application.name}
## dubbo.application.name=${spring.application.name}
# Dubbo Protocol
dubbo.protocol.name=dubbo
dubbo.protocol.port=12345
## Dubbo Registry
dubbo.registry.address=N/A
## DemoService version
demo.service.version=1.0.0
API
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServiceConfig<GreetingsService> service = new ServiceConfig<>();
service.setApplication(new ApplicationConfig("first-dubbo-provider"));
service.setRegistry(new RegistryConfig("multicast://224.5.6.7:1234"));
service.setInterface(GreetingsService.class);
service.setRef(new GreetingsServiceImpl());
service.export();
System.out.println("first-dubbo-provider is running.");
System.in.read();
}
Refer to the sample
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! Please tell us how we can improve.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.
