Dubbo Integrates with Nacos to Become a Registry
Nacos is an important registry in Dubbo ecosystem, and dubbo-registry-nacos is the implementation of Dubbo-integrated Nacos registry.
Preparation Works
Before you integrate dubbo-registry-nacos into your Dubbo project, make sure the Nacos service is started in the background. If you are not familiar with the basic use of Nacos, you can refer to the Quick Start for Nacos: https://nacos.io/en-us/docs/quick-start.html. Nacos versions above 0.6.1 are recommended.
Get Started Quickly
The operation steps for Dubbo to integrate Nacos into a registry are simple, the general steps can be divided into “add Maven dependency” and “configure the registry.”
Increase Maven Dependency
First, you need to add the Maven dependency of dubbo-registry-nacos to your project’s pom.xml file, and it is strongly recommended that you use Dubbo 2.6.5:
<dependencies>
...
<!-- Dubbo Nacos registry dependency -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache</groupId>
<artifactId>dubbo-registry-nacos</artifactId>
<version>0.0.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Keep latest Nacos client version -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.nacos</groupId>
<artifactId>nacos-client</artifactId>
<version>[0.6.1,)</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Dubbo dependency -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache</groupId>
<artifactId>dubbo</artifactId>
<version>2.6.5</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Alibaba Spring Context extension -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.spring</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context-support</artifactId>
<version>1.0.2</version>
</dependency>
...
</dependencies>
When you add dubbo-registry-nacos to your project, you don’t need to programmatically implement the service discovery and registration logic, the actual implementation is provided by the third-party package, and then to configure the Naocs registry.
Configure the Registry
Assuming your Dubbo application is assembled by the Spring Framework, there are two configuration options: Dubbo Spring externalization configuration and Spring XML configuration files, I strongly recommend the former.
Dubbo Spring Externalization Configuration
Dubbo Spring externalization configuration is a new feature introduced by Dubbo 2.5.8, which automatically generates and binds Dubbo configuration Bean through the Spring Environment property, simplifying configuration and lowering the threshold for microservice development.
Assume your Dubbo application uses Zookeeper as the registry and its server IP address is 10.20.153.10, the registered address is also stored in the dubbo-config.properties file as a Dubbo externalization configuration attribute, as shown below:
## application
dubbo.application.name = your-dubbo-application
## Zookeeper registry address
dubbo.registry.address = zookeeper://10.20.153.10:2181
...
Assuming your Nacos Server is also running on server 10.20.153.10 and using the default Nacos service port 8848, you can simply adjust the dubbo.registry.address property as follows:
## 其他属性保持不变
## Nacos registry address
dubbo.registry.address = nacos://10.20.153.10:8848
...
Subsequently, restart your Dubbo application, and Dubbo’s service delivery and consumption information can be displayed in the Nacos console:
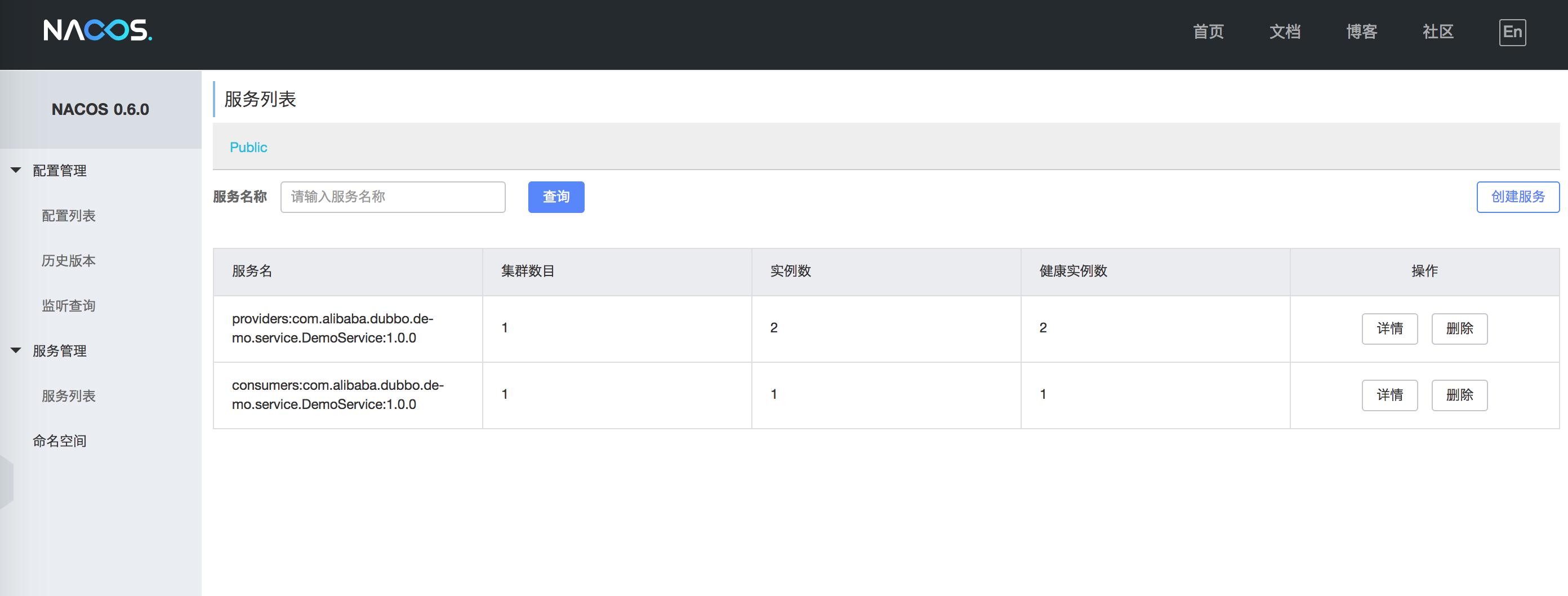
As shown in the figure, the service name prefixed with providers: is the meta-information for the service provider, and consumers: represents the meta-information of the service consumer. Click “Details” to view service status details:
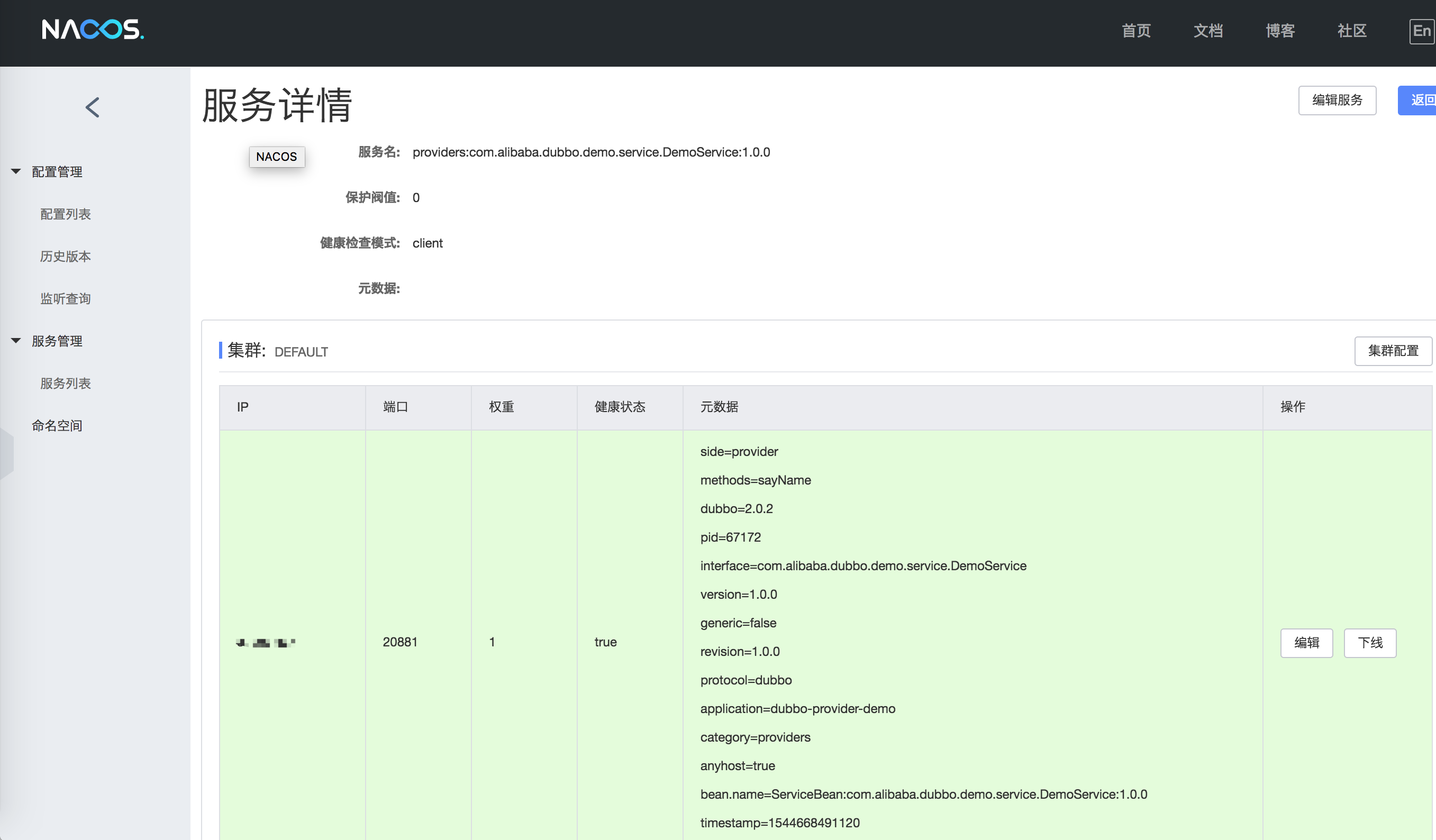
If you are using the Spring XML configuration file to assemble the Dubbo registry, refer to the next section.
Spring XML Configuration File
Also, assume your Dubbo application uses Zookeeper as the registry and its server IP address is 10.20.153.10 and assemble the Spring Bean in an XML file, as shown below:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:dubbo="http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd">
<!-- Provider application information for dependency calculation -->
<dubbo:application name="dubbo-provider-xml-demo" />
<!-- Using the Zookeeper registry Zookeeper -->
<dubbo:registry address="zookeeper://10.20.153.10:2181" />
...
</beans>
Similar to the Dubbo Spring externalization configuration, simply adjust the address property configuration:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:dubbo="http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd">
<!-- Provider application information for dependency calculation-->
<dubbo:application name="dubbo-provider-xml-demo" />
<!-- Using the Nacos registry -->
<dubbo:registry address="nacos://10.20.153.10:8848" />
...
</beans>
Once you restart the Dubbo application, you can also see that the registration meta-information for both service providers and consumers is presented in the Nacos console:
Do you absolutely configure or switch Nacos registry super Easy? If you want to get more or unclear, refer to the complete example below.
Complete Example
The metadata in the above image is derived from the Dubbo Spring annotation-driven example and the Dubbo Spring XML configuration-driven example, both of which will be described below, you can choose your preferred programming model. Before we get into the formal discussion, let’s look at the preparations for both, as they both rely on Java service interfaces and implementations. Also, ensure that the Nacos service is started in the local (127.0.0.1) environment.
Example Interfaces and Implementations
First, define the sample interface, as follows:
package org.apache.dubbo.demo.service;
/**
* DemoService
*
* @since 2.7.4
*/
public interface DemoService {
String sayName(String name);
}
Provide implementation classes for the above interfaces:
package org.apache.dubbo.demo.service;
import org.apache.dubbo.config.annotation.Service;
import org.apache.dubbo.rpc.RpcContext;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
/**
* Default {@link DemoService}
*
* @since 2.7.4
*/
@Service(version = "${demo.service.version}")
public class DefaultService implements DemoService {
@Value("${demo.service.name}")
private String serviceName;
public String sayName(String name) {
RpcContext rpcContext = RpcContext.getContext();
return String.format("Service [name :%s , port : %d] %s(\"%s\") : Hello,%s",
serviceName,
rpcContext.getLocalPort(),
rpcContext.getMethodName(),
name,
name);
}
}
Once the interface and implementation are ready, the annotation-driven and XML configuration-driven implementations will be used below.
Spring Annotation-driven Example
Dubbo 2.7.4 reconstructs the Spring annotation-driven programming model.
Service Provider Annotation-driven Implementation
- Define property source of Dubbo provider externalization configuration - provider-config.properties
## application
dubbo.application.name = dubbo-provider-demo
## Nacos registry address
dubbo.registry.address = nacos://127.0.0.1:8848
## Dubbo Protocol
dubbo.protocol.name = dubbo
dubbo.protocol.port = -1
# Provider @Service version
demo.service.version=1.0.0
demo.service.name = demoService
- Implement service provider bootstrap - DemoServiceProviderBootstrap
package org.apache.dubbo.demo.provider;
import org.apache.dubbo.config.spring.context.annotation.EnableDubbo;
import org.apache.dubbo.demo.service.DemoService;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* {@link DemoService} provider demo
*/
@EnableDubbo(scanBasePackages = "org.apache.dubbo.demo.service")
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:/provider-config.properties")
public class DemoServiceProviderBootstrap {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
context.register(DemoServiceProviderBootstrap.class);
context.refresh();
System.out.println("DemoService provider is starting...");
System.in.read();
}
}
Wherein, the annotation @EnableDubbo activates the Dubbo annotation-driven and externalization configuration, its scanBasePackages property scans the specified Java package, exposes all service interface implementation classes labeled @Service as Spring Bean, and then exports the Dubbo service.
@PropertySource is the standard import property configuration resource annotation introduced by Spring Framework 3.1, which provides externalization configuration for Dubbo.
Service consumer annotation-driven implementation
- Define property source of Dubbo consumer externalization configuration - consumer-config.properties
## Dubbo Application info
dubbo.application.name = dubbo-consumer-demo
## Nacos registry address
dubbo.registry.address = nacos://127.0.0.1:8848
# @Reference version
demo.service.version= 1.0.0
Similarly, the dubbo.registry.address property points to the Nacos registry, through which metadata about other Dubbo services is obtained.
- Implement service consumer bootstrap class - DemoServiceConsumerBootstrap
package org.apache.dubbo.demo.consumer;
import org.apache.dubbo.config.annotation.Reference;
import org.apache.dubbo.config.spring.context.annotation.EnableDubbo;
import org.apache.dubbo.demo.service.DemoService;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* {@link DemoService} consumer demo
*/
@EnableDubbo
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:/consumer-config.properties")
public class DemoServiceConsumerBootstrap {
@Reference(version = "${demo.service.version}")
private DemoService demoService;
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println(demoService.sayName("小马哥(mercyblitz)"));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
context.register(DemoServiceConsumerBootstrap.class);
context.refresh();
context.close();
}
}
Similarly, the @EnableDubbo annotation activates the Dubbo annotation-driven and externalization configuration, although it currently belongs to the service consumer and does not require the Java package name to scan the service implementation labeled @Service.
@Reference is a dependency injection annotation for Dubbo remote services that requires service provider and consumer contract interface, version, and group information. In the current service consumption example, the service version of DemoService is derived from the property configuration file consumer-config.properties.
The @PostConstruct code shows that when the DemoServiceConsumerBootstrap Bean is initialized, it executes ten Dubbo remote method invocation.
Run the Annotation-driven Example
Start DemoServiceProviderBootstrap twice locally and the registry will have two health services:

Run DemoServiceConsumerBootstrap again and the results are as follows:
Service [name :demoService , port : 20880] sayName("小马哥(mercyblitz)") : Hello,小马哥(mercyblitz)
Service [name :demoService , port : 20881] sayName("小马哥(mercyblitz)") : Hello,小马哥(mercyblitz)
Service [name :demoService , port : 20880] sayName("小马哥(mercyblitz)") : Hello,小马哥(mercyblitz)
Service [name :demoService , port : 20880] sayName("小马哥(mercyblitz)") : Hello,小马哥(mercyblitz)
Service [name :demoService , port : 20881] sayName("小马哥(mercyblitz)") : Hello,小马哥(mercyblitz)
Service [name :demoService , port : 20881] sayName("小马哥(mercyblitz)") : Hello,小马哥(mercyblitz)
Service [name :demoService , port : 20880] sayName("小马哥(mercyblitz)") : Hello,小马哥(mercyblitz)
Service [name :demoService , port : 20880] sayName("小马哥(mercyblitz)") : Hello,小马哥(mercyblitz)
Service [name :demoService , port : 20881] sayName("小马哥(mercyblitz)") : Hello,小马哥(mercyblitz)
Service [name :demoService , port : 20881] sayName("小马哥(mercyblitz)") : Hello,小马哥(mercyblitz)
Run correctly and the service consumer uses a load balancing strategy to allocate ten RPC calls equally to two Dubbo service provider instances.
Spring XML Configuration-driven Example
Spring XML configuration-driven is the programming model of traditional Spring assembly components.
Service Provider XML Configuration-driven
Define the service provider XML context configuration file - /META-INF/spring/dubbo-provider-context.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:dubbo="http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd">
<!--
Provider application information for dependency calculation
-->
<dubbo:application name="dubbo-provider-xml-demo"/>
<!-- Using the Nacos registry -->
<dubbo:registry address="nacos://127.0.0.1:8848"/>
<!-- Using Dubbo protocol to expose services on random ports -->
<dubbo:protocol name="dubbo" port="-1"/>
<!-- Declare the service interface to be exposed -->
<dubbo:service interface="org.apache.dubbo.demo.service.DemoService" ref="demoService" version="2.0.0"/>
<!-- Implement services like local beans -->
<bean id="demoService" class="org.apache.dubbo.demo.service.DefaultService"/>
</beans>
- Implement service provider bootstrap class - DemoServiceProviderBootstrap
package org.apache.dubbo.demo.provider;
import org.apache.dubbo.demo.service.DemoService;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* {@link DemoService} provider demo XML bootstrap
*/
public class DemoServiceProviderXmlBootstrap {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext();
context.setConfigLocation("/META-INF/spring/dubbo-provider-context.xml");
context.refresh();
System.out.println("DemoService provider (XML) is starting...");
System.in.read();
}
}
Service Consumer XML Configuration-driven
Define the consumer provider XML context configuration file - /META-INF/spring/dubbo- consumer-context.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:dubbo="http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd">
<!--
Provider application information for dependency calculation
-->
<dubbo:application name="dubbo-consumer-xml-demo"/>
<!-- Using the Nacos registry-->
<dubbo:registry address="nacos://127.0.0.1:8848"/>
<!-- Reference service interface -->
<dubbo:reference id="demoService" interface="org.apache.dubbo.demo.service.DemoService" version="2.0.0"/>
</beans>
- Implement service consumer bootstrap class - DemoServiceConsumerBootstrap
package org.apache.dubbo.demo.consumer;
import org.apache.dubbo.demo.service.DemoService;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* {@link DemoService} consumer demo XML bootstrap
*/
public class DemoServiceConsumerXmlBootstrap {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext();
context.setConfigLocation("/META-INF/spring/dubbo-consumer-context.xml");
context.refresh();
System.out.println("DemoService consumer (XML) is starting...");
DemoService demoService = context.getBean("demoService", DemoService.class);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println(demoService.sayName("小马哥(mercyblitz)"));
}
context.close();
}
}
Run XML Configuration-driven Example
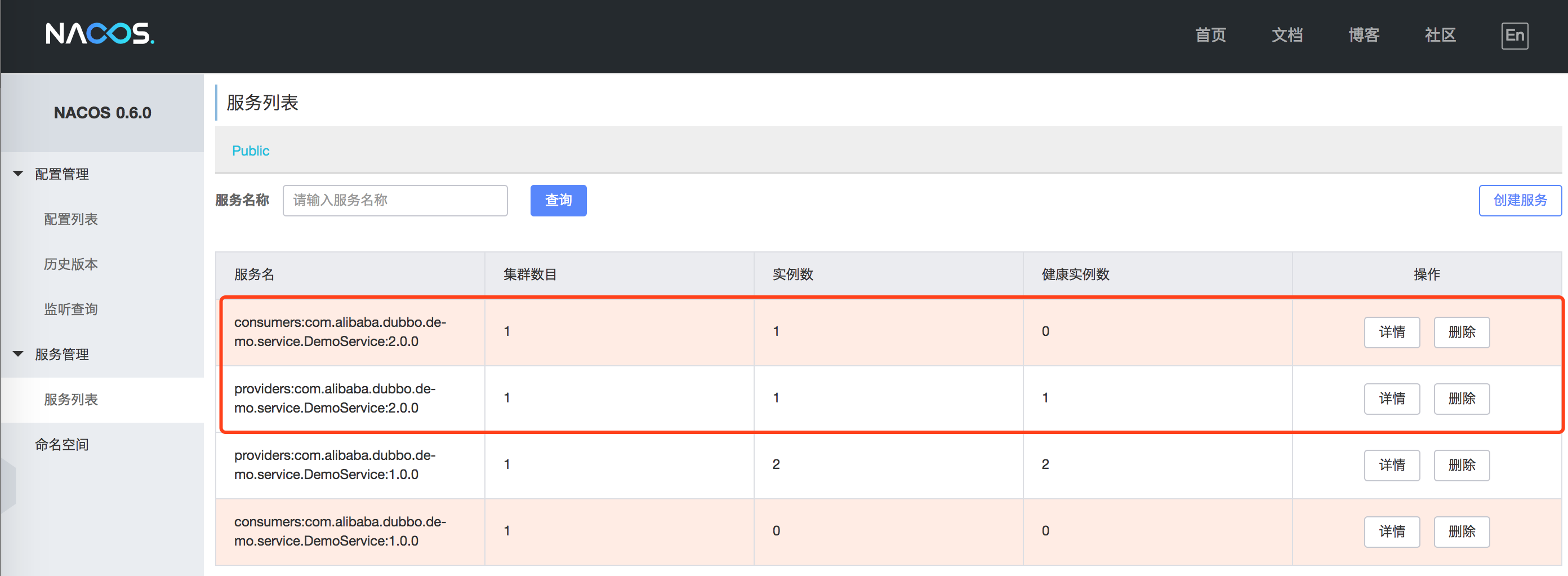
As such, start two DemoServiceProviderXmlBootstrap bootstraps and observe the changes in the Nacos registry service provider:

The service version driven by the XML configuration is 2.0.0, so the registration service is correct.
Run the service consumer bootstrap DemoServiceConsumerXmlBootstrap again and observe the console output:
Service [name :null , port : 20882] sayName("小马哥(mercyblitz)") : Hello,小马哥(mercyblitz)
Service [name :null , port : 20882] sayName("小马哥(mercyblitz)") : Hello,小马哥(mercyblitz)
Service [name :null , port : 20883] sayName("小马哥(mercyblitz)") : Hello,小马哥(mercyblitz)
Service [name :null , port : 20882] sayName("小马哥(mercyblitz)") : Hello,小马哥(mercyblitz)
Service [name :null , port : 20882] sayName("小马哥(mercyblitz)") : Hello,小马哥(mercyblitz)
Service [name :null , port : 20883] sayName("小马哥(mercyblitz)") : Hello,小马哥(mercyblitz)
Service [name :null , port : 20882] sayName("小马哥(mercyblitz)") : Hello,小马哥(mercyblitz)
Service [name :null , port : 20883] sayName("小马哥(mercyblitz)") : Hello,小马哥(mercyblitz)
Service [name :null , port : 20883] sayName("小马哥(mercyblitz)") : Hello,小马哥(mercyblitz)
Service [name :null , port : 20883] sayName("小马哥(mercyblitz)") : Hello,小马哥(mercyblitz)
As a result, both operation and load balancing are normal due to the property demo.service.name has not been added to the current example, the “name” information is output as null. For more information, please refer to: https://github.com/apache/dubbo/tree/master/dubbo-registry/dubbo-registry-nacos.
If you’re interested in or fond of open source projects like Dubbo and Nacos, try clicking “star” to support them. The links are as follows:
- Apache Dubbo: https://github.com/apache/dubbo
- Dubbo Nacos Registry: https://github.com/apache/dubbo/tree/master/dubbo-registry/dubbo-registry-nacos
- Alibaba Nacos: https://github.com/alibaba/nacos
