Dubbo Basic Usage -- Dubbo Provider Configuration
This chapter mainly talking about how to configure dubbo. According to the configuration mode, it can be divided into the following mode: XML Configuration, Properties Configuration, Annotation Configuration, API Invocation Mode Configuration. And according to the function, we can divide them into Dubbo Provider and Dubbo Consumer. In the following sections, we would explain Dubbo Provider and Dubbo Consumer respectively.
Dubbo Provider Configuration
Provider Configuration in Detail
The configuration mode of Dubbo Provider has 4 different ways: XML Configuration, Properties Configuration, API Invocation Mode Configuration and Annotation Configuration.
XML Configuration
The simplest configuration example:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:dubbo="http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd">
<dubbo:application name="hello-world-app" />
<dubbo:registry address="multicast://224.5.6.7:1234" />
<dubbo:protocol name="dubbo" port="20880" />
<dubbo:service interface="com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService" ref="demoServiceLocal" />
<dubbo:reference id="demoServiceRemote" interface="com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService" />
</beans>
In the example above,note the way to write dubbo schema:
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:dubbo="http://code.alibabatech.com/schema/dubbo"
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd
http://code.alibabatech.com/schema/dubbo http://code.alibabatech.com/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd">
Supported Configuration Tags
| Tags | Application | Describe |
|---|---|---|
| <dubbo:service/> | Service Configuration | Expose a service, define the meta information of the service. One service can use multiple protocols to expose and can be registered to multiple registry centers |
| <dubbo:reference/> | Reference Configuration | Create a remote service agent, one reference can point to multiple registry centers |
| <dubbo:protocol/> | Protocol Configuration | Configure protocol information for providing services, protocol is specified by the provider and accepted passively by the consumer |
| <dubbo:application/> | Application Configuration | Configure current application information, regardless of whether the application is provider or consumer |
| <dubbo:module/> | Module Configuration | Configure current module information. Optional |
| <dubbo:registry/> | Registry Center Configuration | Configure information related to connect registry centers |
| <dubbo:monitor/> | Monitoring Center Configuration | Configure information related to connect monitor centers. Optional |
| <dubbo:provider/> | Provider Configuration | When some properties ProtocolConfig or ServiceConfig are not configured, use this default value. Optional |
| <dubbo:consumer/> | Consumer Configuration | When some properties of ReferenceConfig are not configured, use this default value. Optional |
| <dubbo:method/> | Method Configuration | Configure specific method level information of ServiceConfig and ReferenceConfig |
| <dubbo:argument/> | Parameter Configuration | Configure parameters of specific method |
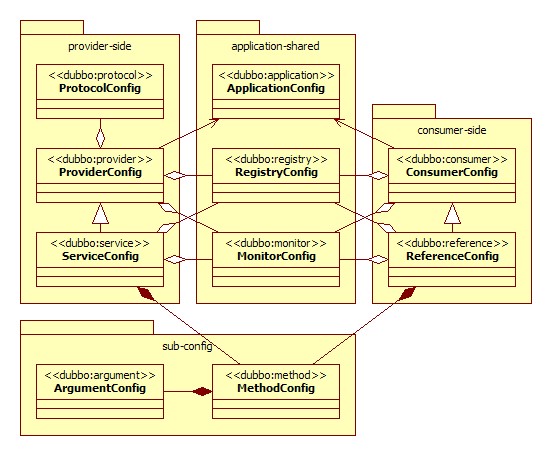
Configuration Diagram
Configuration item in detail
<dubbo:application name=“hello-world-app” />
Apply to specific application name, note that you need to make sure that the application name is unique. The application name can be displayed in the following console admin for easy management.<dubbo:registry address=“multicast://224.5.6.7:1234” />
Configure registry center, related to the specific mechanism of service discovery. It can be zookeeper address or eureka address. The address above is the broadcast address, which is very convenient in the test process of the local service invocation.<dubbo:protocol name=“dubbo” port=“20880” />
Here is the transport protocol and the default port, generally no changes are required.
Next, we will focus on the configuration of <dubbo:service/>
- <dubbo:service/>mainly supports the following properties:
| Properties Name | Description |
|---|---|
| version | Version number |
| scope | Service visibility, value can be local or remote,remote by default |
| actives | Maximum number of activated requests |
| async | Whether the method called asynchronously,false by default |
| cache | Service cache,optional value:lru/threadlocal/jcache |
| callbacks | Limitation of callback instance |
| generic | Generalized calls which can be bypassed |
| class | The implementation of the service’s class name |
| connections | The number of connections in the service |
| delay | The number of milliseconds delay for publicating the service |
| executes | Upper bound of service execution requests |
| retries | Timeout retry times |
| timeout | Invocation timeout time |
For other configuration properties, please refer to xsd:http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd
- <dubbo:method/> as the sub-element of <dubbo:service/> can be configured corresponding to method. Properties that are commonly used are:
| Properties Name | Description |
|---|---|
| executes | Upper bound of service execution requests |
| retries | Timeout retry times |
| timeout | Invocation timeout time |
For other properties,you can refer to xsd above。
Configuration Override Relationship
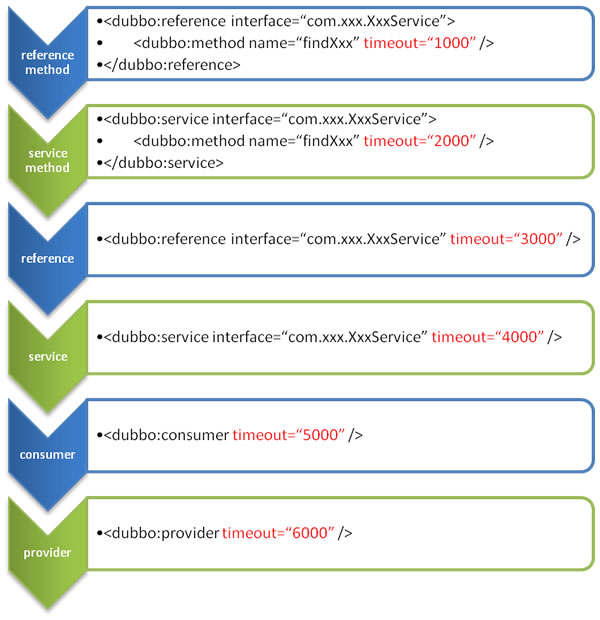
Configuration Coverage Relationship Diagram
The Override relationship here includes the configuration of both provider end and consumer end. If you have any questions about consumer, you can refer to the next chapter, consumer chapter, to understand.
dubbo.properties Configuration
If the public configuration is very simple, no multiple registry centers, no multiple protocols, etc., or if you want multiple Spring containers to share the configuration, you can use dubbo.properties as the default configurations.
Dubbo would load dubbo.properties under the classpath root directory automaticaly,you can change the default configuration location by JVM startup parameter -Ddubbo.properties.file=xxx.properties.
dubbo.properties Configuration example
# application name
dubbo.application.name=dubbodemo-provider
# registry center address
dubbo.registry.address=zookeeper://localhost:2181
# Example of broadcasting registry center
#dubbo.registry.address=multicast://224.5.6.7:1234
# address for calling protocol
dubbo.protocol.name=dubbo
dubbo.protocol.port=28080
Mapping Rule
Split the tag name and properties in XML configuration with dots, and multiple properties should be split into multiple lines
- For example: dubbo.application.name=foo equivalents to <dubbo:application name=“foo” />
- For example: dubbo.registry.address=10.20.153.10:9090 equivalents to <dubbo:registry address=“10.20.153.10:9090” />
If there are multiple configurations having the same tag name, they can be distinguished by id, and if there is no id, the configurations will be applied to all tags with the same name.
- For example: dubbo.protocol.rmi.port=1234 equivalents to <dubbo:protocol id=“rmi” name=“rmi” port=“1234” />
- For example: dubbo.registry.china.address=10.20.153.10:9090 equivalents to <dubbo:registry id=“china” address=“10.20.153.10:9090” />
Coverage Strategy

- When JVM starts, -D parameter has priority, so that users can rewrite the parameters when deploy and start, for example, the protocol port should be changed when start.
- Then comes to XML, the configurations in dubbo.properties are invalid, if they are configured in XML.
- Properties are the last, which can be considered as default value. Only when there is no configuration in XML, the corresponding configuarations in dubbo.properties will become effective, which usually applies to shared public configuration, like application name.
Note:
- If there are multiple dubbo.properties in the classpath root directory, for example, if dubbo.properties exist in multiple JAR files, Dubbo will load anyone arbitrarily and print the Error logs, which may change to throwing exceptions later.↩
- When the protocol’s id is not configured, protocol name will be used as id as default.
Annotation
Service Annotation Exposure Service
import com.alibaba.dubbo.config.annotation.Service;
@Service(timeout = 5000)
public class AnnotateServiceImpl implements AnnotateService {
// ...
}
Javaconfig Configuration Public Module
@Configuration
public class DubboConfiguration {
@Bean
public ApplicationConfig applicationConfig() {
ApplicationConfig applicationConfig = new ApplicationConfig();
applicationConfig.setName("provider-test");
return applicationConfig;
}
@Bean
public RegistryConfig registryConfig() {
RegistryConfig registryConfig = new RegistryConfig();
registryConfig.setAddress("zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181");
registryConfig.setClient("curator");
return registryConfig;
}
}
The result of configuration using this method is the same as that of using xml.
Specify the Dubbo Scan Path
@SpringBootApplication
@DubboComponentScan(basePackages = "com.alibaba.dubbo.test.service.impl")
public class ProviderTestApp {
// ...
}
or use the spring bean xml configuration:
<dubbo:annotation package="com.chanshuyi.service.impl" />
API Trigger Directly
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.config.ApplicationConfig;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.config.RegistryConfig;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.config.ProviderConfig;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.config.ServiceConfig;
import com.xxx.XxxService;
import com.xxx.XxxServiceImpl;
// Service implementation
XxxService xxxService = new XxxServiceImpl();
// current application configuration
ApplicationConfig application = new ApplicationConfig();
application.setName("xxx");
// connect to registry center configuration
RegistryConfig registry = new RegistryConfig();
registry.setAddress("10.20.130.230:9090");
registry.setUsername("aaa");
registry.setPassword("bbb");
// service provider's protocol configuration
ProtocolConfig protocol = new ProtocolConfig();
protocol.setName("dubbo");
protocol.setPort(12345);
protocol.setThreads(200);
// Note: ServiceConfig is a heavy object, which encapsulated the connection with registry center internally, and open the service port
// Service provider exposes service configuration
ServiceConfig<XxxService> service = new ServiceConfig<XxxService>(); // This instance is very heavy, which encapsulated the connection with registry center, please cache it by yourself, it might cause memory and connection leakage otherwise.
service.setApplication(application);
service.setRegistry(registry); // multiple registry centers can use setRegistries()
service.setProtocol(protocol); // multiple protocols can use setProtocols()
service.setInterface(XxxService.class);
service.setRef(xxxService);
service.setVersion("1.0.0");
// exposure and register service
service.export();
Generally, this method is not recommended in spring applications. The reason can be checked by reading the source code on github, which would not be explained here.
Provider Interface and Implement
The above chapters are described mainly from a configuration perspective, and lets explain the complete use of Dubbo provider by going through a complete example.
There is only one service UserReadService, and one method getUserById in this example. This service need to be exposed to a remote service by Dubbo. Detail steps are shown below:
- Create Project Skip this step if there is already a project. Create a Spring Boot project, which can be created through https://start.spring.io/.
- Define Interface Define interface: UserReadService
public interface UserReadService{
public User getUserById(Long userId);
}
Generally, this interface should be placed in an independent JAR file as a client package. Generally, the other services need to refer this client package if they want to consume this service(except for generalized call). 3. Implement Interface Implement UserReadService, and deploy current implementation in the Provider’s application.
public UserReadServiceImpl implements UserReadService{
public User getUserById(Long userId){
return xxx;
}
}
- Dubbo Configuration
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:dubbo="http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd">
<dubbo:application name="hello-world-app" />
<dubbo:registry address="multicast://224.5.6.7:1234" />
<dubbo:protocol name="dubbo" port="20880" />
<bean id="userReadService" class="com.package.UserReadServiceImpl"/>
<dubbo:service interface="com.package.UserReadService" ref="userReadService" />
</beans>
For the other modes of Dubbo configuration, please refer to the related configurations in the previous chapter, or use the integrated Dubbo Spring Boot starter method.
